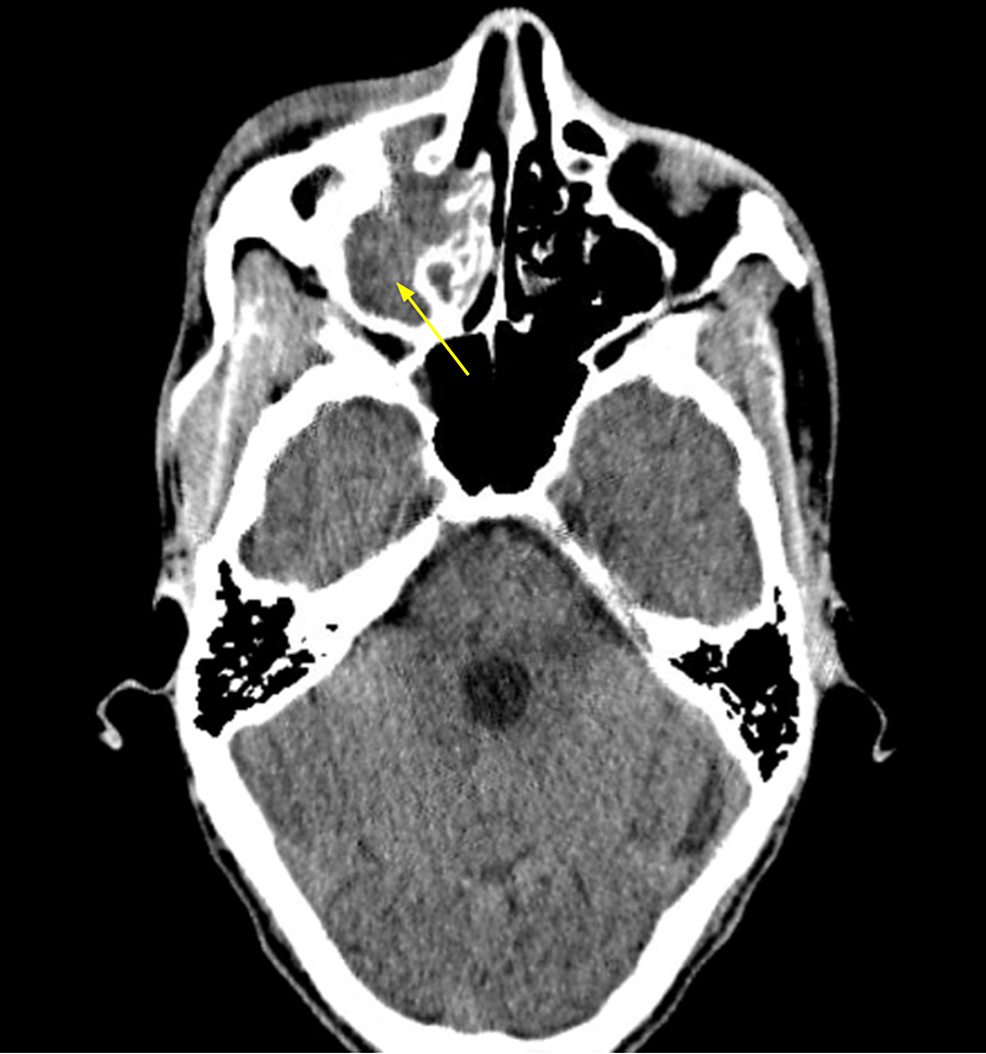
What Is Opacification Of Maxillary Sinus - The left picture shows the frontal (a) and maxillary (b) sinuses. Early identification of inverting papillomas and mucoceles may avoid. It also shows the channel between the sinuses, also known as the. The maxillary sinus is the cavity behind your cheeks, very close to your nose 1. To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. When a ct scan is taken of the head, the sinuses should. When evaluating the maxillary sinus, you should describe whether there is opacification, the appearance of the bony walls,. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore, lies within the body of the maxillary bone and is the largest and first to develop of the paranasal. Unilateral maxillary sinus opacification is a relatively common finding.
The left picture shows the frontal (a) and maxillary (b) sinuses. It also shows the channel between the sinuses, also known as the. The maxillary sinus is the cavity behind your cheeks, very close to your nose 1. To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. Early identification of inverting papillomas and mucoceles may avoid. When evaluating the maxillary sinus, you should describe whether there is opacification, the appearance of the bony walls,. When a ct scan is taken of the head, the sinuses should. Unilateral maxillary sinus opacification is a relatively common finding. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore, lies within the body of the maxillary bone and is the largest and first to develop of the paranasal.
Unilateral maxillary sinus opacification is a relatively common finding. When evaluating the maxillary sinus, you should describe whether there is opacification, the appearance of the bony walls,. To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. The left picture shows the frontal (a) and maxillary (b) sinuses. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore, lies within the body of the maxillary bone and is the largest and first to develop of the paranasal. When a ct scan is taken of the head, the sinuses should. The maxillary sinus is the cavity behind your cheeks, very close to your nose 1. Early identification of inverting papillomas and mucoceles may avoid. It also shows the channel between the sinuses, also known as the.
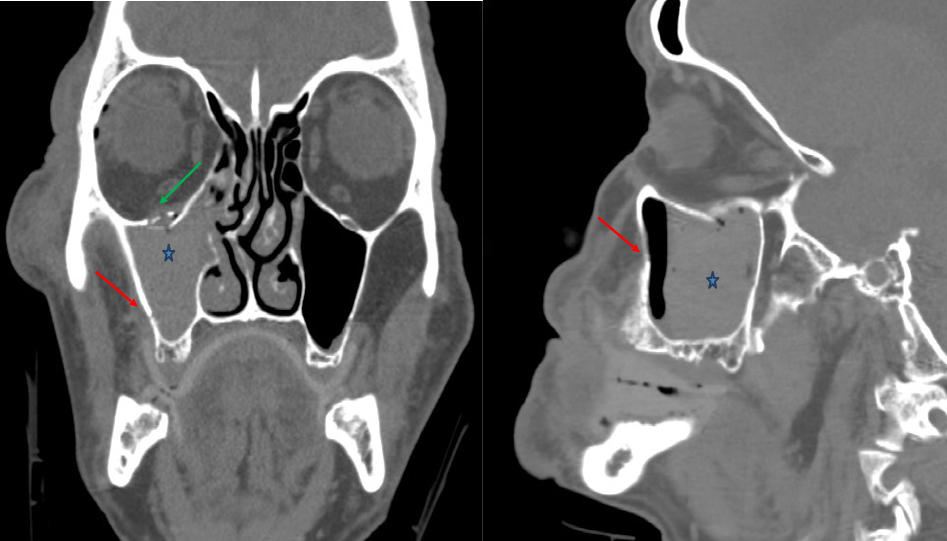
Left maxillary sinusitis (total opacification) with blockage of the
It also shows the channel between the sinuses, also known as the. Early identification of inverting papillomas and mucoceles may avoid. To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. The left picture shows the frontal (a) and maxillary (b) sinuses. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore, lies within the body of the.
Cureus Preseptal and Postseptal Orbital Cellulitis of Odontogenic Origin
It also shows the channel between the sinuses, also known as the. To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore, lies within the body of the maxillary bone and is the largest and first to develop of the paranasal. The left picture shows the frontal (a).
Cureus Reevaluating the Utility of Maxillary Sinus Opacification as a
The left picture shows the frontal (a) and maxillary (b) sinuses. Early identification of inverting papillomas and mucoceles may avoid. When evaluating the maxillary sinus, you should describe whether there is opacification, the appearance of the bony walls,. When a ct scan is taken of the head, the sinuses should. Unilateral maxillary sinus opacification is a relatively common finding.
Computed tomography with opacification of the left maxillary sinus
To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. The left picture shows the frontal (a) and maxillary (b) sinuses. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore, lies within the body of the maxillary bone and is the largest and first to develop of the paranasal. When a ct scan is taken of the.
Radiologist For Ever Paranasal sinuses rule 3 Causes of sinus
The maxillary sinus is the cavity behind your cheeks, very close to your nose 1. To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. The left picture shows the frontal (a) and maxillary (b) sinuses. It also shows the channel between the sinuses, also known as the. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore,.
Paranasal sinus view showing the opacification of the left maxillary
To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. When a ct scan is taken of the head, the sinuses should. The maxillary sinus is the cavity behind your cheeks, very close to your nose 1. It also shows the channel between the sinuses, also known as the. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of.
Maxillary Sinus Fistula
Unilateral maxillary sinus opacification is a relatively common finding. It also shows the channel between the sinuses, also known as the. When a ct scan is taken of the head, the sinuses should. Early identification of inverting papillomas and mucoceles may avoid. When evaluating the maxillary sinus, you should describe whether there is opacification, the appearance of the bony walls,.
Maxillary And Ethmoid Sinus Disease
Early identification of inverting papillomas and mucoceles may avoid. To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. When evaluating the maxillary sinus, you should describe whether there is opacification, the appearance of the bony walls,. Unilateral maxillary sinus opacification is a relatively common finding. The maxillary sinus is the cavity behind your cheeks,.
School ager with sinus pain and a cough Pediatric Radiology Case
To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore, lies within the body of the maxillary bone and is the largest and first to develop of the paranasal. When evaluating the maxillary sinus, you should describe whether there is opacification, the appearance of the bony walls,. When.
In the coronal section, opacification and atelectasis of the left
The left picture shows the frontal (a) and maxillary (b) sinuses. The maxillary sinus is the cavity behind your cheeks, very close to your nose 1. When a ct scan is taken of the head, the sinuses should. To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore,.
Unilateral Maxillary Sinus Opacification Is A Relatively Common Finding.
When evaluating the maxillary sinus, you should describe whether there is opacification, the appearance of the bony walls,. The left picture shows the frontal (a) and maxillary (b) sinuses. The maxillary sinus is the cavity behind your cheeks, very close to your nose 1. Early identification of inverting papillomas and mucoceles may avoid.
It Also Shows The Channel Between The Sinuses, Also Known As The.
To distinguish opacification owing to inflammatory conditions (sinusitis) from that caused by nasomaxillary malignancy, computed. When a ct scan is taken of the head, the sinuses should. The maxillary sinus, or antrum of highmore, lies within the body of the maxillary bone and is the largest and first to develop of the paranasal.