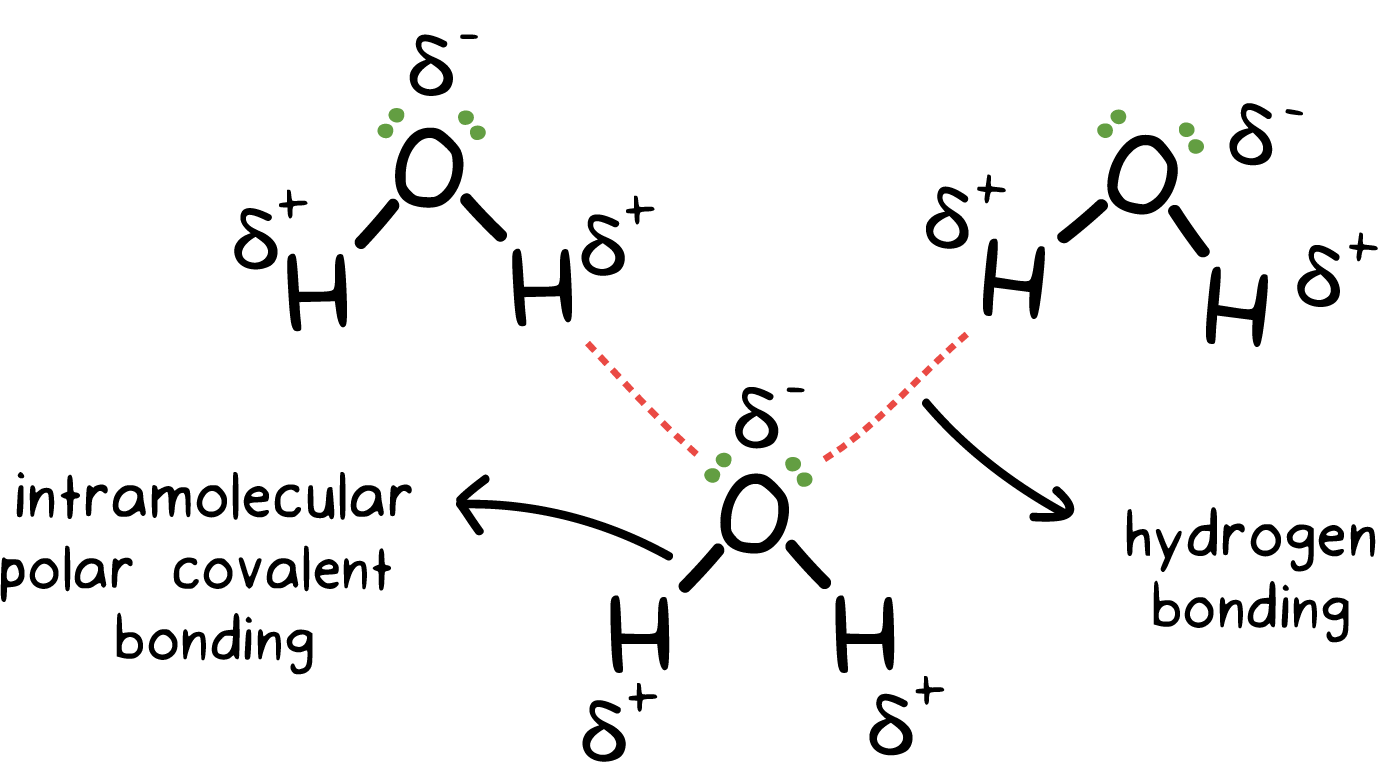
What Intermolecular Forces Are Present In Nh3 - Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force. In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. London dispersion and hydrogen bonds. In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces.
In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces. In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. London dispersion and hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force.
London dispersion and hydrogen bonds. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes. In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces.
Intermolecular Forces for NH3 (Ammonia) YouTube
The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force. In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces.
SOLVED Identify the intermolecular forces present in each of these
The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces. London dispersion and hydrogen bonds. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force.
H2S Intermolecular Forces (Strong or Weak) Techiescientist
The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force. London dispersion and hydrogen bonds. In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen.
Image result for intermolecular forces Chemie
In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force. London dispersion and hydrogen bonds.
Intermolecular Forces in Chemistry
In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. London dispersion and hydrogen bonds. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force.
intermolecular vs. intramolecular forces Diagram Quizlet
In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force. In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces.
vapor pressure intermolecular forces
In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes. In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force.
intermolecular force of nh3
London dispersion and hydrogen bonds. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force. In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces.
Solved The intermolecular forces present in NH3 include
In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces. London dispersion and hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen.
SOLVED NH3, has the same molecular shape as PCl3. Which intermolecular
In ammonia (nh3), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding and london dispersion forces. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force. The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes. The types of intermolecular forces present in ammonia, or nh3, are hydrogen bonds. London dispersion and hydrogen bonds.
In Ammonia (Nh3), The Intermolecular Forces Present Are Hydrogen Bonding And London Dispersion Forces.
In nh3 (ammonia), the intermolecular forces present are hydrogen bonding, which occurs between the hydrogen. London dispersion and hydrogen bonds. Every molecule experiences london dispersion as an intermolecular force. The hydrogen bonds are many magnitudes.