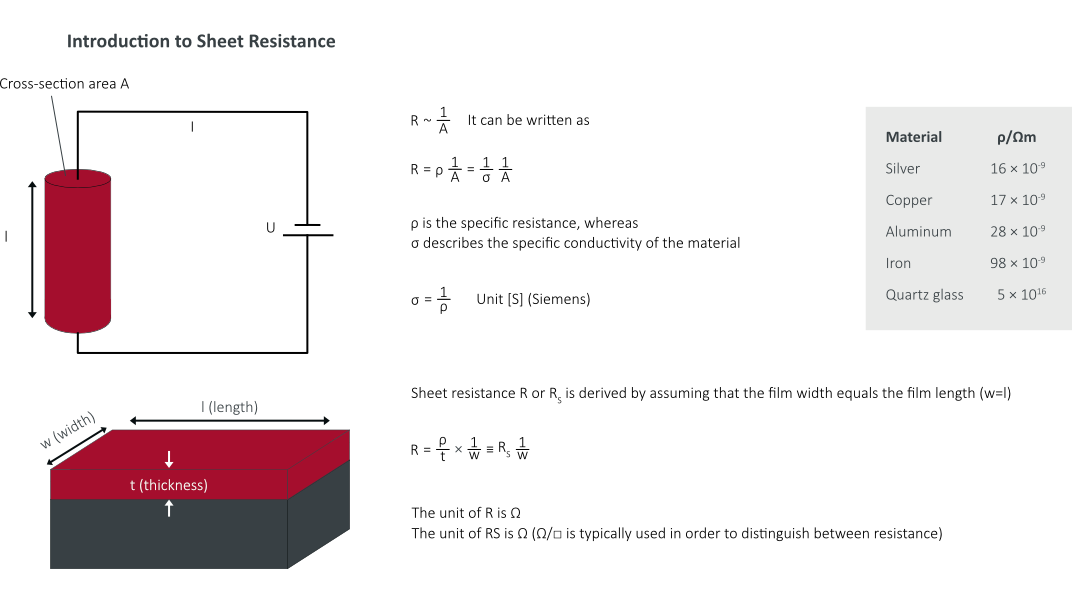
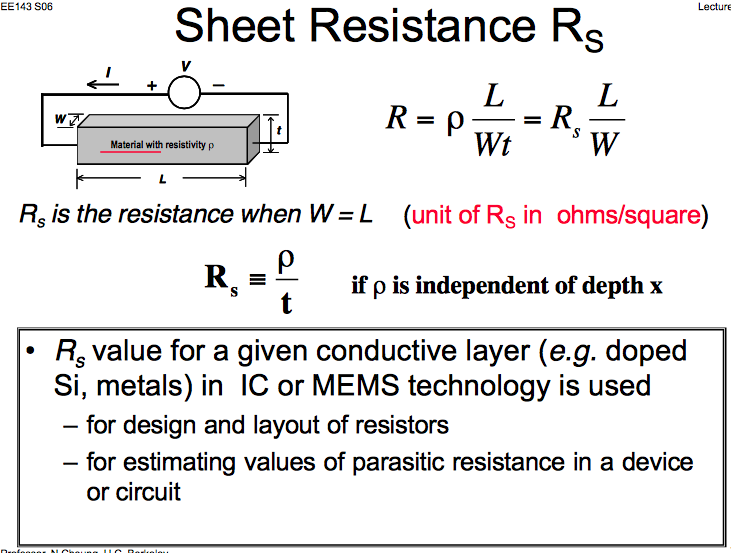
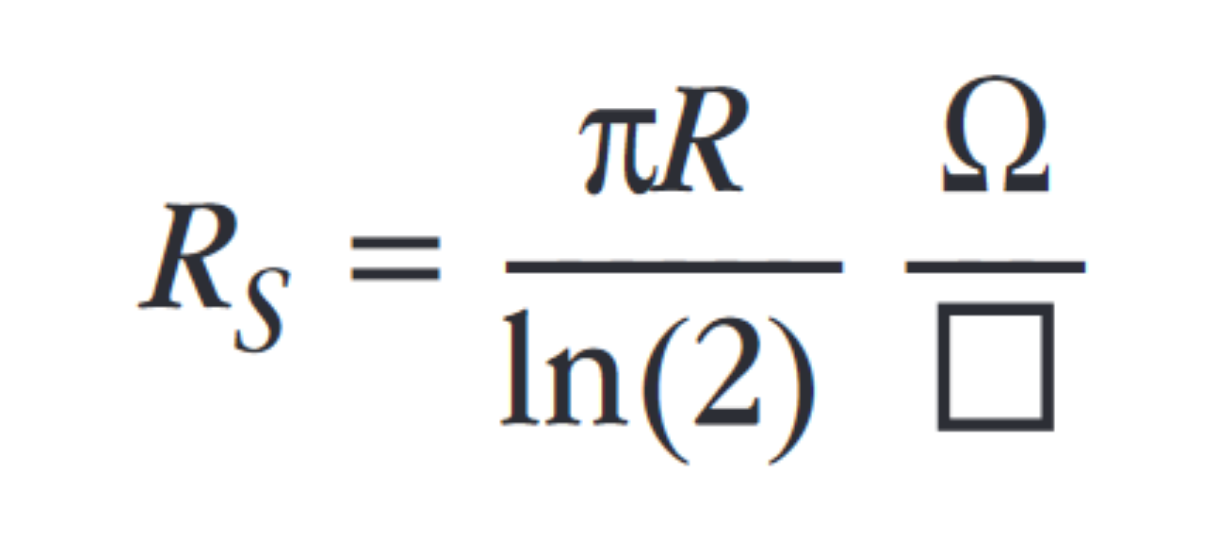Sheet Resistance Formula - Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a uniform sheet thickness. Four point probe based instruments use a long established technique to measure the average resistance of a thin layer or sheet by passing current through the outside two points of the probe and. R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes, and i is the current applied between. Frequently you do not know t. The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: Commonly, resistivity (also known as bulk resistivity, specific electrical resistivity, or volume resistivity) is in units of. Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3.
Commonly, resistivity (also known as bulk resistivity, specific electrical resistivity, or volume resistivity) is in units of. Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3. The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: Frequently you do not know t. Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a uniform sheet thickness. R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes, and i is the current applied between. Four point probe based instruments use a long established technique to measure the average resistance of a thin layer or sheet by passing current through the outside two points of the probe and.
Four point probe based instruments use a long established technique to measure the average resistance of a thin layer or sheet by passing current through the outside two points of the probe and. Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a uniform sheet thickness. R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes, and i is the current applied between. Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3. The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: Commonly, resistivity (also known as bulk resistivity, specific electrical resistivity, or volume resistivity) is in units of. Frequently you do not know t.
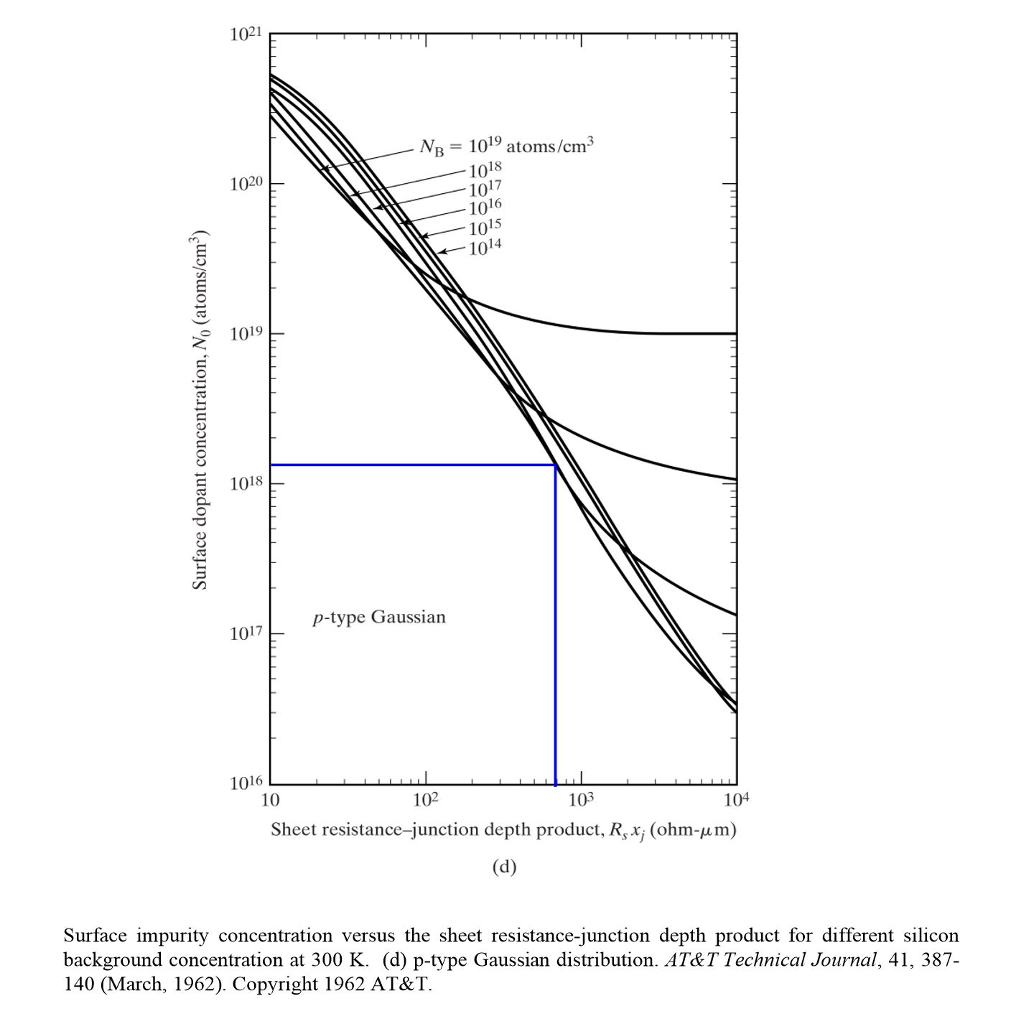
1. Sheet Resistance In extrinsic material, the sheet
The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes, and i is the current applied between. Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3. Commonly, resistivity (also known as bulk resistivity, specific electrical resistivity, or volume.
L8B What is Sheet Resistance; Calculate Sheet Resistance YouTube
The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a uniform sheet thickness. Four point probe based instruments use a long established technique to measure the average resistance of a thin layer or sheet by passing current through the outside two points of the probe and. Commonly, resistivity (also.
What is the difference between resistance and resistivity?
The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: Frequently you do not know t. Four point probe based instruments use a long established technique to measure the average resistance of a thin layer or sheet by passing current through the outside two points of the probe and. Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a.
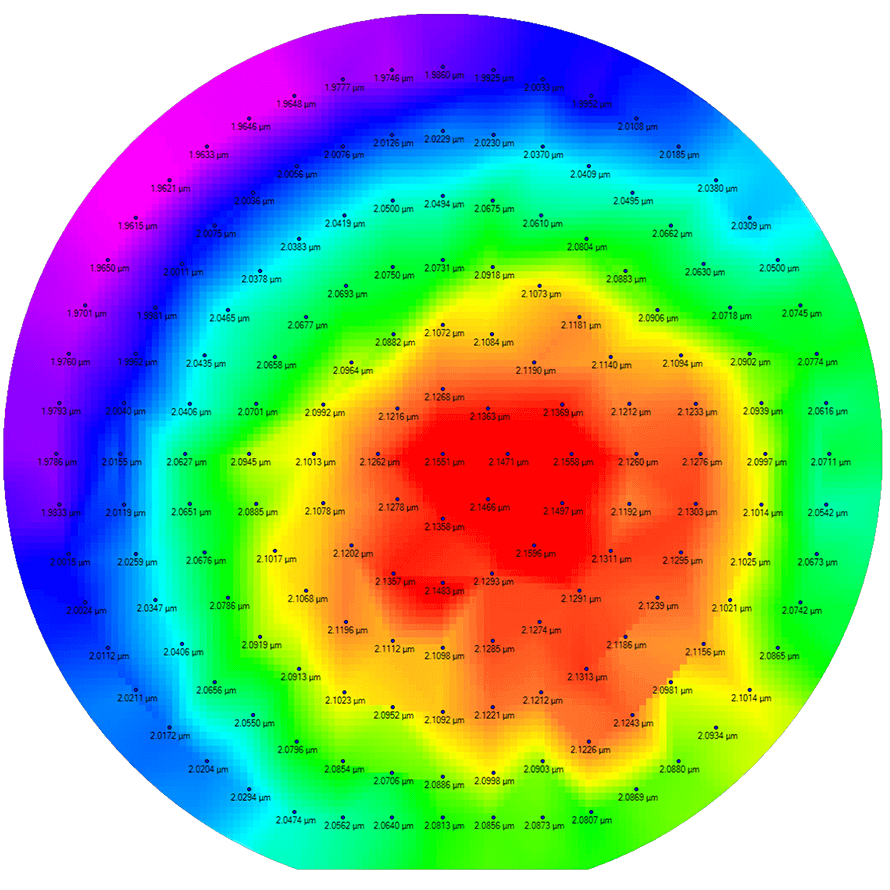
Sheet Resistance Mapping Solutions for research on Surfaces and
Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a uniform sheet thickness. R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes, and i is the current applied between. The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: Frequently you do not know t. Current in 1 & out 4.
SURAGUS Information on Sheet Resistance Measurement
Commonly, resistivity (also known as bulk resistivity, specific electrical resistivity, or volume resistivity) is in units of. Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3. Frequently you do not know t. R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes, and i is the current applied between..
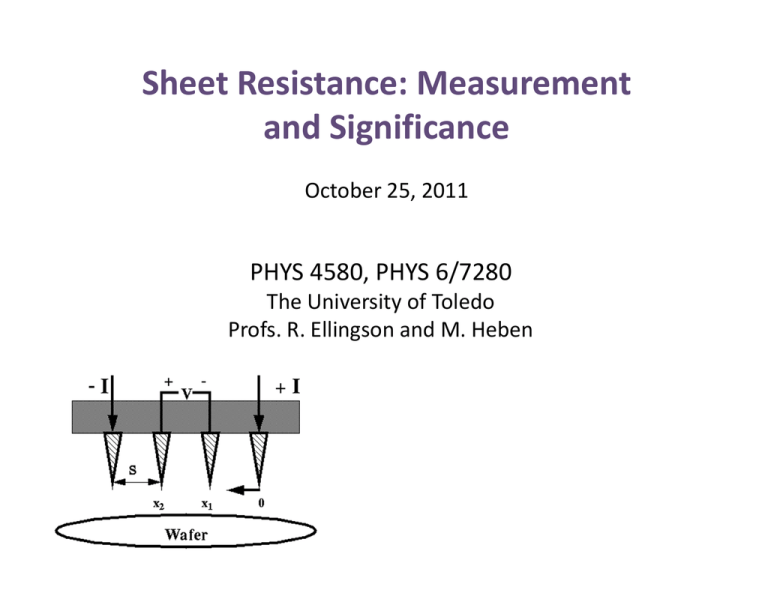
Sheet Resistance Measurement and Significance
Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3. The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: Frequently you do not know t. Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a uniform sheet thickness. R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes,.
Sheet Resistance
Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3. Four point probe based instruments use a long established technique to measure the average resistance of a thin layer or sheet by passing current through the outside two points of the probe and. R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between.
EE143 S06 Lecture Sheet Resistance Rs R p WIt
Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3. R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes, and i is the current applied between. Four point probe based instruments use a long established technique to measure the average resistance of a thin layer or sheet by passing.
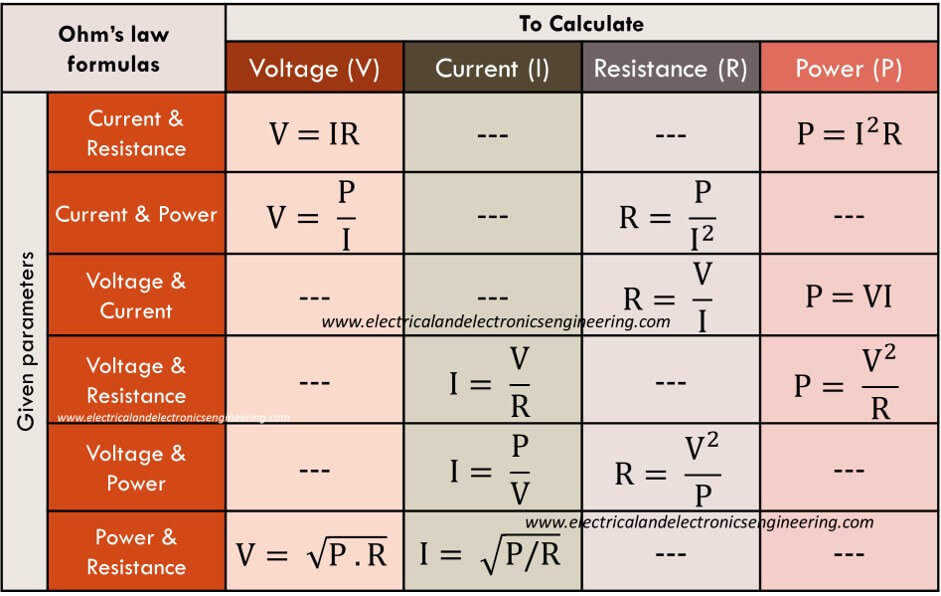
Ohm's Law Formula Sheet Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3. Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a uniform sheet thickness. Frequently you do not know t. The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: Commonly, resistivity (also known as bulk resistivity, specific electrical resistivity, or volume resistivity) is in units of.
Performing van der Pauw Sheet Resistance Measurements Using the
R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes, and i is the current applied between. Commonly, resistivity (also known as bulk resistivity, specific electrical resistivity, or volume resistivity) is in units of. Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a uniform sheet thickness. Current in 1 & out 4.
Frequently You Do Not Know T.
Four point probe based instruments use a long established technique to measure the average resistance of a thin layer or sheet by passing current through the outside two points of the probe and. Sheet resistance is a special case of resistivity for a uniform sheet thickness. Current in 1 & out 4 and voltage measured on 2 and 3. R s is the sheet resistance, δv is the change in voltage measured between the inner probes, and i is the current applied between.
Commonly, Resistivity (Also Known As Bulk Resistivity, Specific Electrical Resistivity, Or Volume Resistivity) Is In Units Of.
The sheet resistance can then be calculated using the following equation: