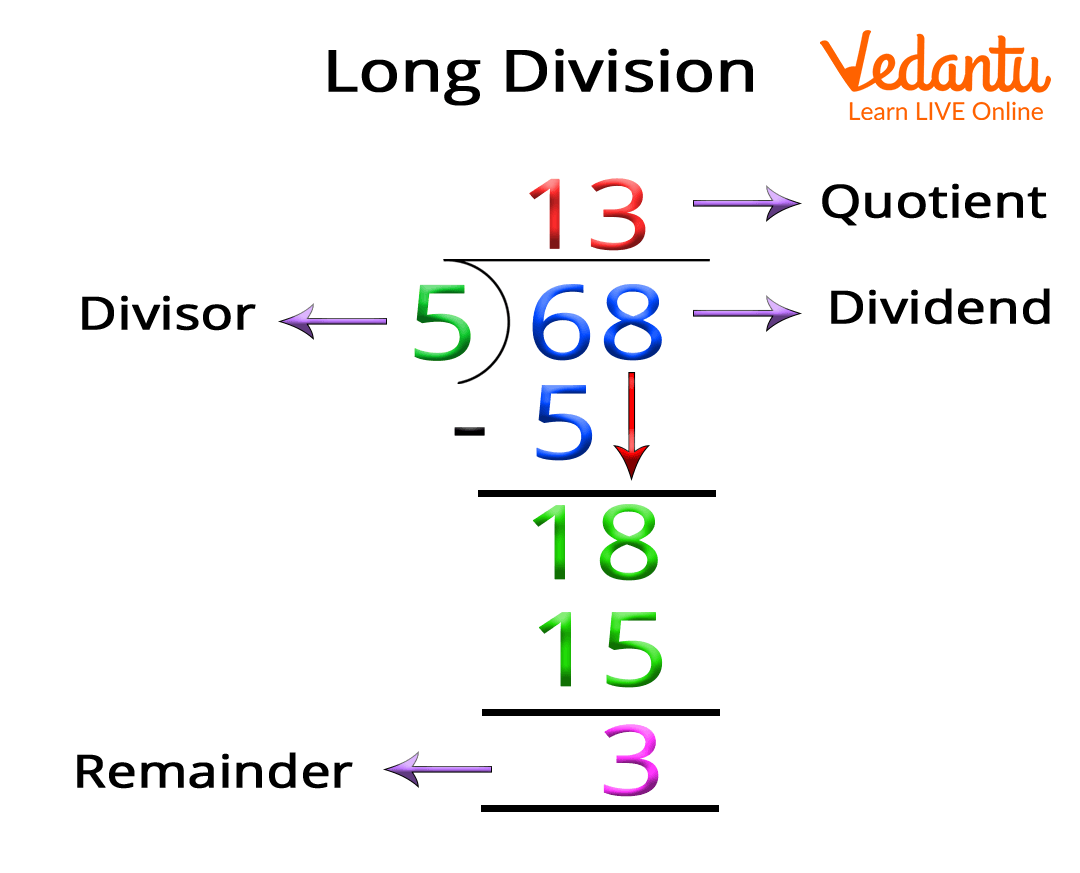
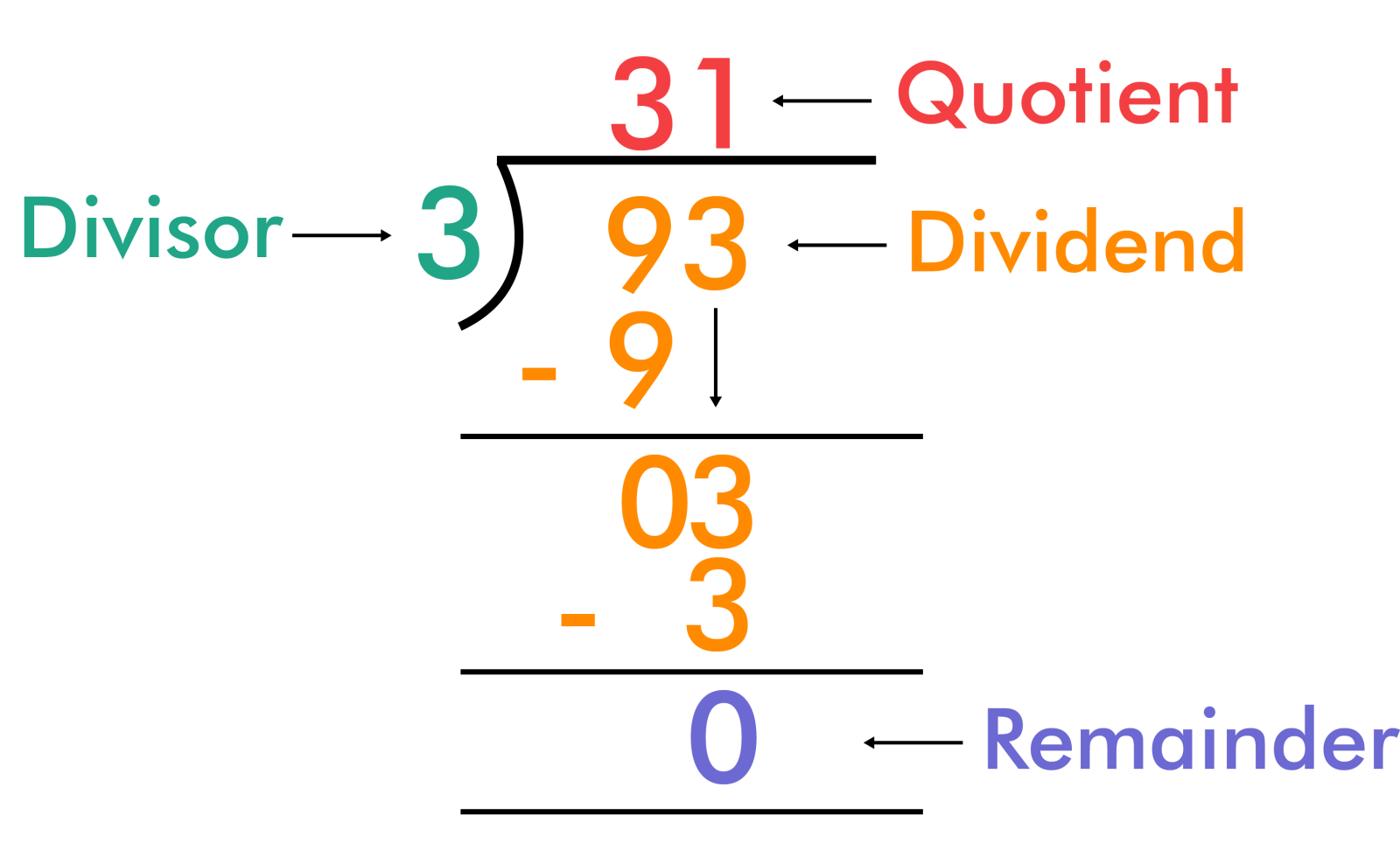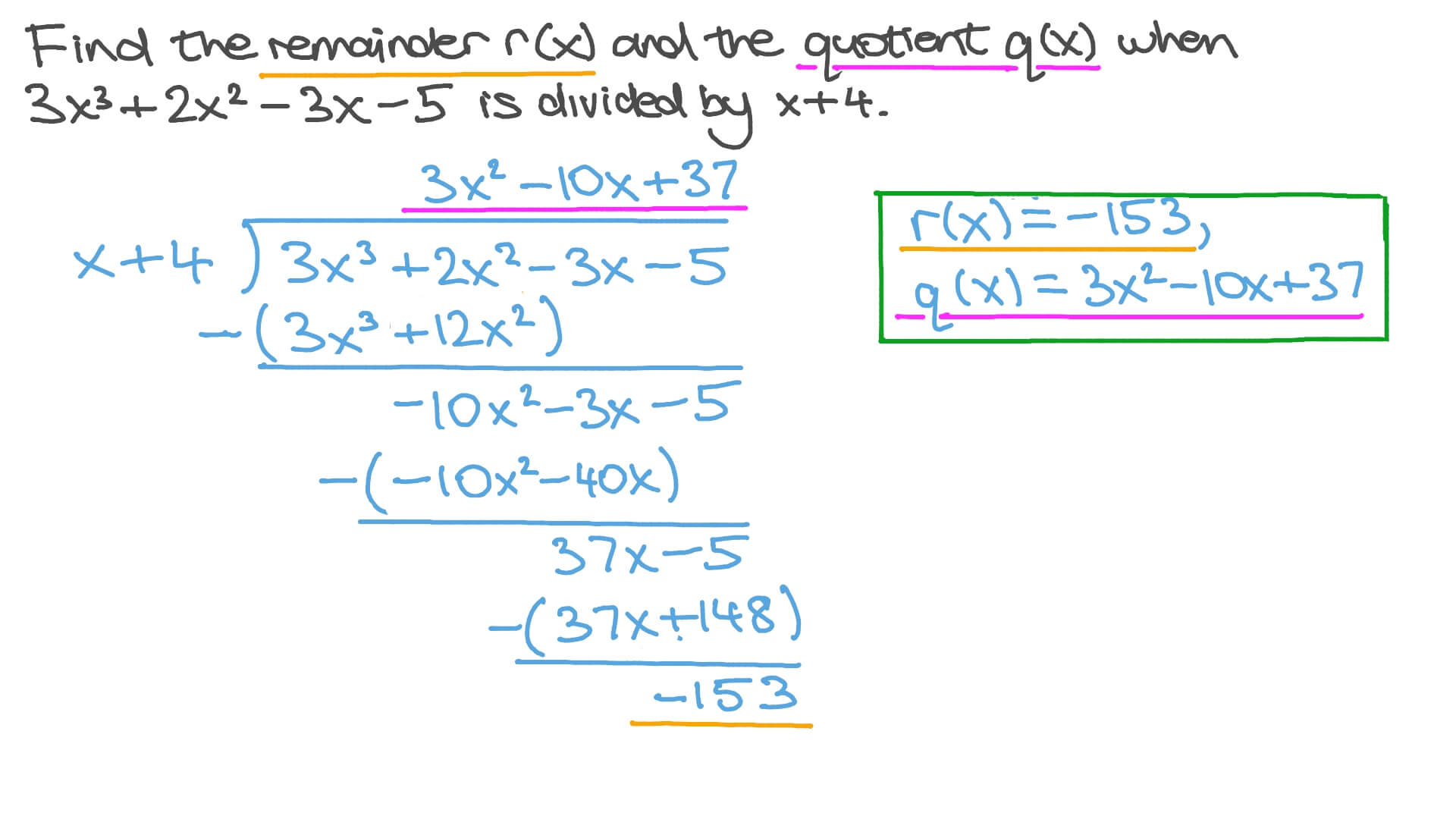Quotient Remainder Form - Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that: When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b | such that a = b · q + r and we define a / / b : When dividends are not split evenly by the divisor, then the leftover part is the remainder. N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <.
When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. When dividends are not split evenly by the divisor, then the leftover part is the remainder. Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b | such that a = b · q + r and we define a / / b : N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <. Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that:
Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that: When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b | such that a = b · q + r and we define a / / b : When dividends are not split evenly by the divisor, then the leftover part is the remainder. N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <.
What is a Remainder in Math? (Definition, Examples) BYJUS
When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <. When dividends are not split evenly by the divisor, then the leftover part is the remainder. Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that: Quotient function given two integers a ,.
Remainder Definition, Facts & Examples
Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b | such that a = b · q + r and we define a / / b : When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. N.
What is a Remainder in Math? (Definition, Examples) BYJUS
Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that: When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <. When dividends are not split evenly by the divisor, then the leftover part is the remainder. Quotient function given two integers a ,.
Question Video Finding a Quotient and Remainder from a Polynomial
Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that: When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b |.
Writing Polynomials in (Divisor)(Quotient) + Remainder Form
N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <. Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that: Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b.
How to write it in quotient + remainder/divisor form
When dividends are not split evenly by the divisor, then the leftover part is the remainder. Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b | such that a = b · q + r and we.
The Remainder Theorem Top Online General
Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b | such that a = b · q + r and we define a / / b : N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <..
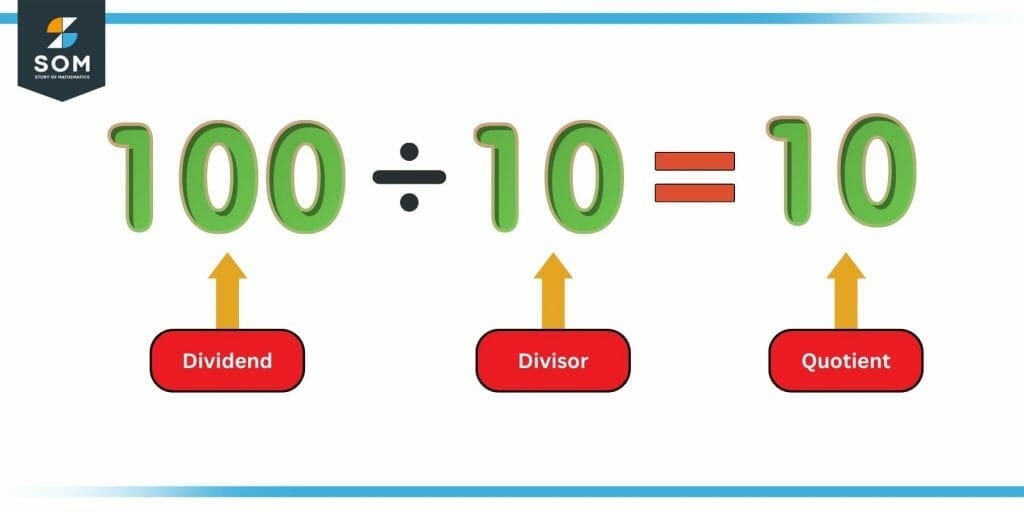
Quotient Definition & Meaning
N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <. When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b | such that a = b · q +.
Division With Remainders Examples
When dividends are not split evenly by the divisor, then the leftover part is the remainder. When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that: N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <. Quotient function given two integers a ,.
PPT Division of Polynomials PowerPoint Presentation ID272069
Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that: When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. Quotient function given two integers a , b ∈ ℤ such that b ≠ 0 , then we get some q , r ∈ ℤ with 0 ≤ r < | b |.
Quotient Function Given Two Integers A , B ∈ ℤ Such That B ≠ 0 , Then We Get Some Q , R ∈ ℤ With 0 ≤ R < | B | Such That A = B · Q + R And We Define A / / B :
When we divide 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is. Given any integer n and a positive integer d, there exist unique integers q and r such that: N = d⋅q + r, and 0 ≤ r <. When dividends are not split evenly by the divisor, then the leftover part is the remainder.