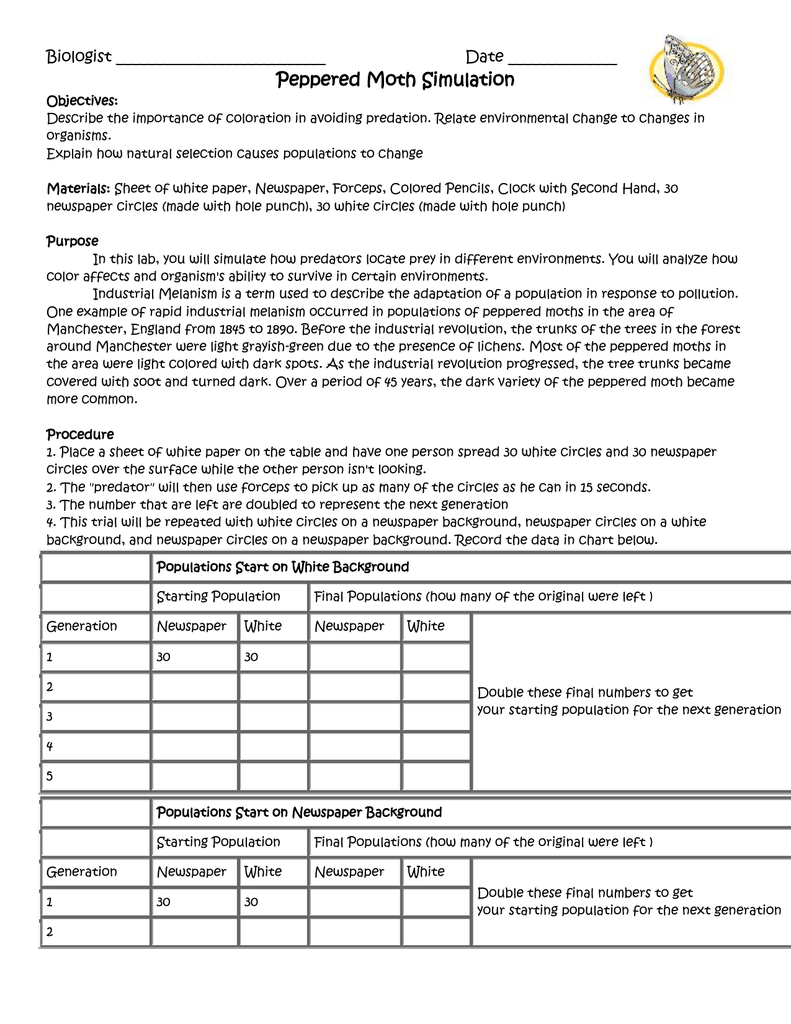
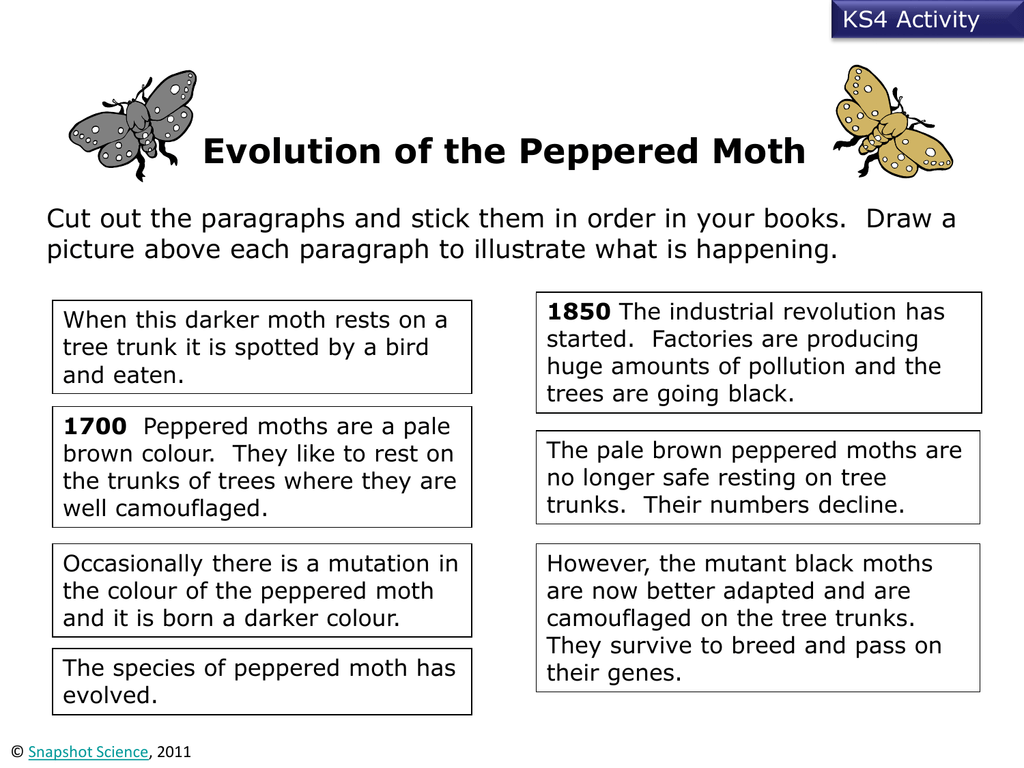
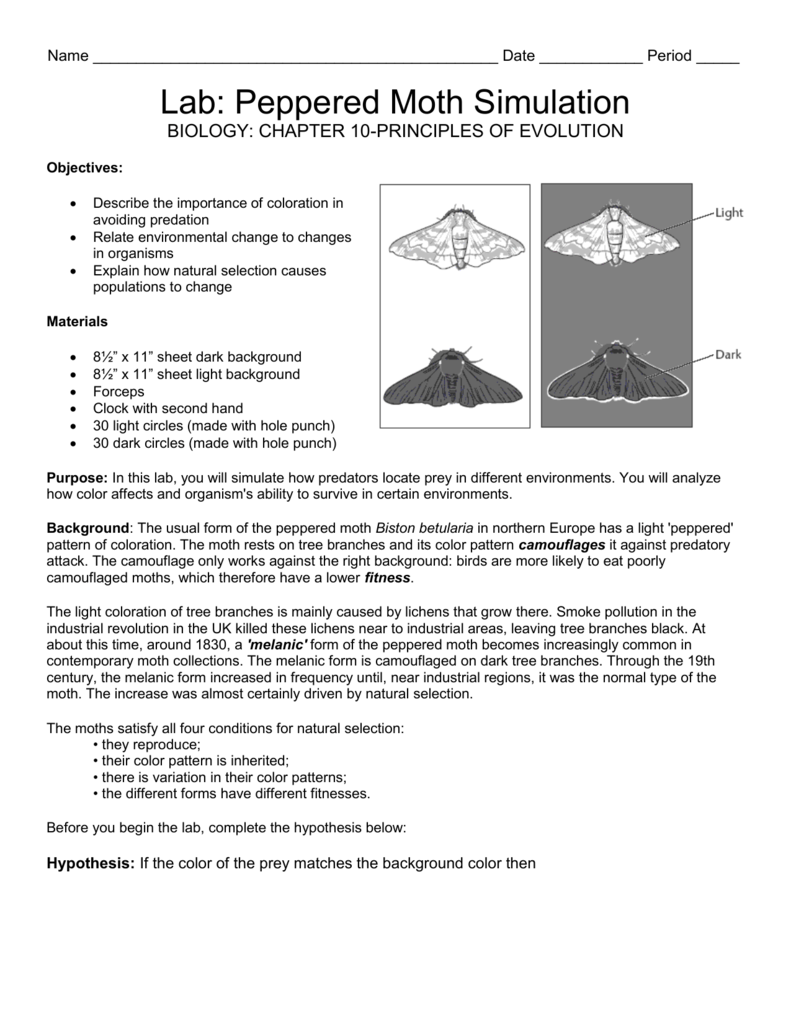
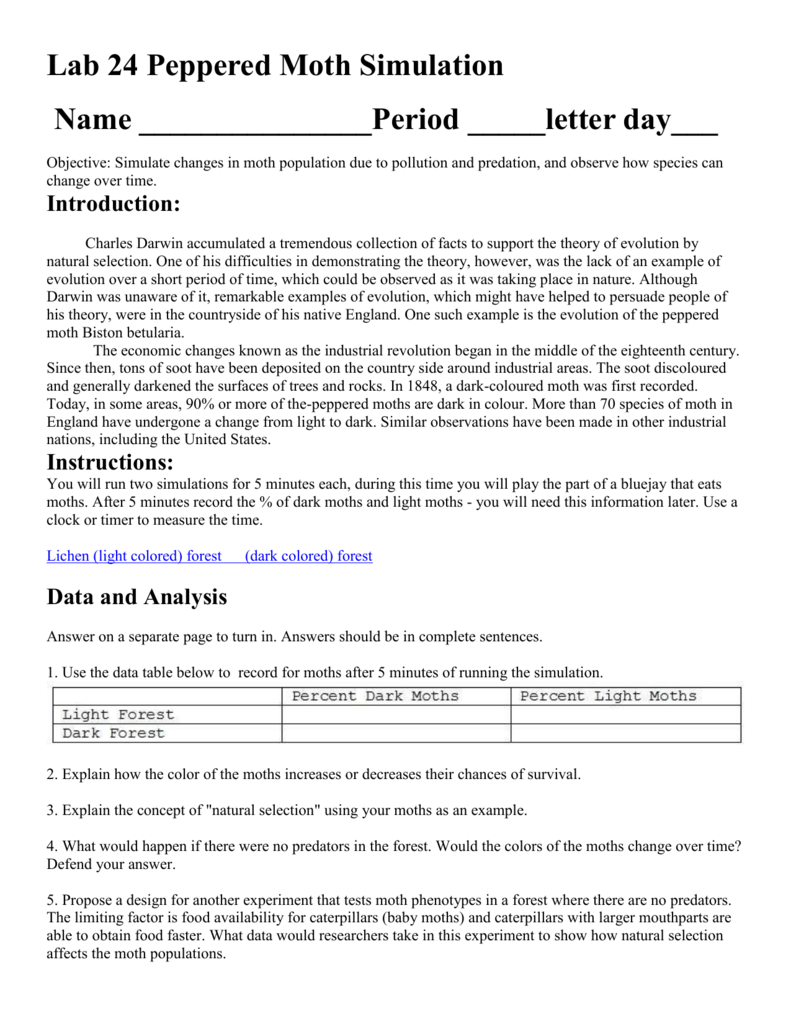
Peppered Moth Simulation Worksheet - Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england. Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation. How do peppered moths avoid predators? Where are peppered moths found? Modern evolution theory states that if the frequency of genes in a population changes. This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. What is the difference between carbonia and insularia. Observe how species can change over time by playing a bluebird eating.
Where are peppered moths found? This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. Modern evolution theory states that if the frequency of genes in a population changes. Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation. Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england. Observe how species can change over time by playing a bluebird eating. How do peppered moths avoid predators? What is the difference between carbonia and insularia.
Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england. Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation. What is the difference between carbonia and insularia. How do peppered moths avoid predators? Modern evolution theory states that if the frequency of genes in a population changes. Where are peppered moths found? This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. Observe how species can change over time by playing a bluebird eating.
Peppered Moth Simulation Lab
This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england. What is the difference between carbonia and insularia. Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation. How do peppered moths avoid predators?
Peppered Moth Simulation Answer Key Exploring Evolutionary Mechanisms
How do peppered moths avoid predators? This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. Where are peppered moths found? What is the difference between carbonia and insularia. Modern evolution theory states that if the frequency of genes in a population changes.
pepperedmoth Snapshot Science
How do peppered moths avoid predators? Modern evolution theory states that if the frequency of genes in a population changes. This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation. Where are peppered moths found?
Lab Peppered Moth Simulation
Where are peppered moths found? How do peppered moths avoid predators? Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation. What is the difference between carbonia and insularia. Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england.
The Peppered Moth hsc biology Evolutionary Biology Biological
What is the difference between carbonia and insularia. Observe how species can change over time by playing a bluebird eating. How do peppered moths avoid predators? Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england. Where are peppered moths found?
SOLUTION Peppered moth natural selection questions Studypool
Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england. What is the difference between carbonia and insularia. How do peppered moths avoid predators? Observe how species can change over time by playing a bluebird eating. Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation.
Free peppered moth worksheet, Download Free peppered moth worksheet png
Where are peppered moths found? How do peppered moths avoid predators? This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. Observe how species can change over time by playing a bluebird eating. Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation.
Peppered Moth Simulation
This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. Modern evolution theory states that if the frequency of genes in a population changes. Observe how species can change over time by playing a bluebird eating. What is the difference between carbonia and insularia. Simulate changes in moth.
Peppered Moth Simulation
Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation. Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england. How do peppered moths avoid predators? This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. Observe how species can change over time by playing a bluebird eating.
The Peppered Moth Simulation Worksheet Answer Key
Modern evolution theory states that if the frequency of genes in a population changes. Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england. Where are peppered moths found? This activity introduces three environments (light gray, medium gray, and dark gray) and three moth genotypes resulting in the expression of three. How do peppered moths avoid predators?
Observe How Species Can Change Over Time By Playing A Bluebird Eating.
Simulate changes in moth population due to pollution and predation. How do peppered moths avoid predators? What is the difference between carbonia and insularia. Find out how the peppered moth surprised naturalists in england.
This Activity Introduces Three Environments (Light Gray, Medium Gray, And Dark Gray) And Three Moth Genotypes Resulting In The Expression Of Three.
Where are peppered moths found? Modern evolution theory states that if the frequency of genes in a population changes.