Microseconds To Milliseconds - Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds. I believe that you are missing the.count();. Std::chrono::milliseconds d = std::chrono::duration_cast< std::chrono::milliseconds >( fs ); To break the code into details, paste the below code into a python console: The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent. The usleep() function suspends execution of the calling thread for (at least) usec microseconds. Well, actually, the legacy class java.sql.timestamp attempts to represent. Java 8 captures the current moment in milliseconds, while a new clock implementation in java 9 captures the moment in finer granularity, typically microseconds though it depends on the.
I believe that you are missing the.count();. The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent. The usleep() function suspends execution of the calling thread for (at least) usec microseconds. Well, actually, the legacy class java.sql.timestamp attempts to represent. Java 8 captures the current moment in milliseconds, while a new clock implementation in java 9 captures the moment in finer granularity, typically microseconds though it depends on the. To break the code into details, paste the below code into a python console: Std::chrono::milliseconds d = std::chrono::duration_cast< std::chrono::milliseconds >( fs ); Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds.
Std::chrono::milliseconds d = std::chrono::duration_cast< std::chrono::milliseconds >( fs ); The usleep() function suspends execution of the calling thread for (at least) usec microseconds. Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds. Java 8 captures the current moment in milliseconds, while a new clock implementation in java 9 captures the moment in finer granularity, typically microseconds though it depends on the. Well, actually, the legacy class java.sql.timestamp attempts to represent. I believe that you are missing the.count();. To break the code into details, paste the below code into a python console: The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent.
Microseconds To Seconds
Java 8 captures the current moment in milliseconds, while a new clock implementation in java 9 captures the moment in finer granularity, typically microseconds though it depends on the. The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent. Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds. Std::chrono::milliseconds d = std::chrono::duration_cast<.
Convert From Microseconds To Milliseconds
Java 8 captures the current moment in milliseconds, while a new clock implementation in java 9 captures the moment in finer granularity, typically microseconds though it depends on the. The usleep() function suspends execution of the calling thread for (at least) usec microseconds. To break the code into details, paste the below code into a python console: Furthermore, as others.
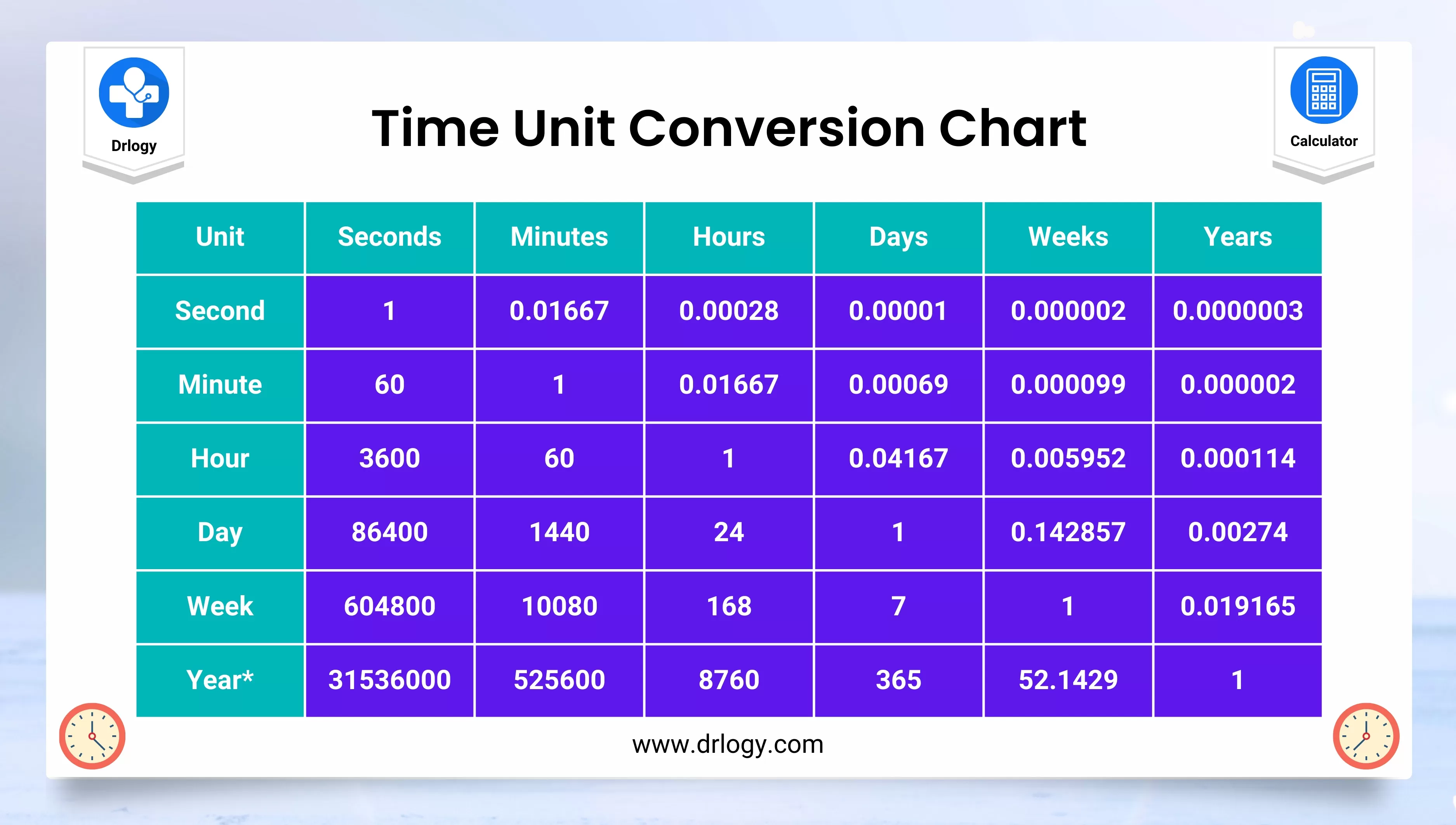
Best Time Unit Converter Calcualtor Time Calculator Drlogy
Std::chrono::milliseconds d = std::chrono::duration_cast< std::chrono::milliseconds >( fs ); The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent. Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds. I believe that you are missing the.count();. The usleep() function suspends execution of the calling thread for (at least) usec microseconds.
Unveiling the World of Precise Time Measurement Exploring the
Std::chrono::milliseconds d = std::chrono::duration_cast< std::chrono::milliseconds >( fs ); I believe that you are missing the.count();. Java 8 captures the current moment in milliseconds, while a new clock implementation in java 9 captures the moment in finer granularity, typically microseconds though it depends on the. Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds. The usleep() function suspends.
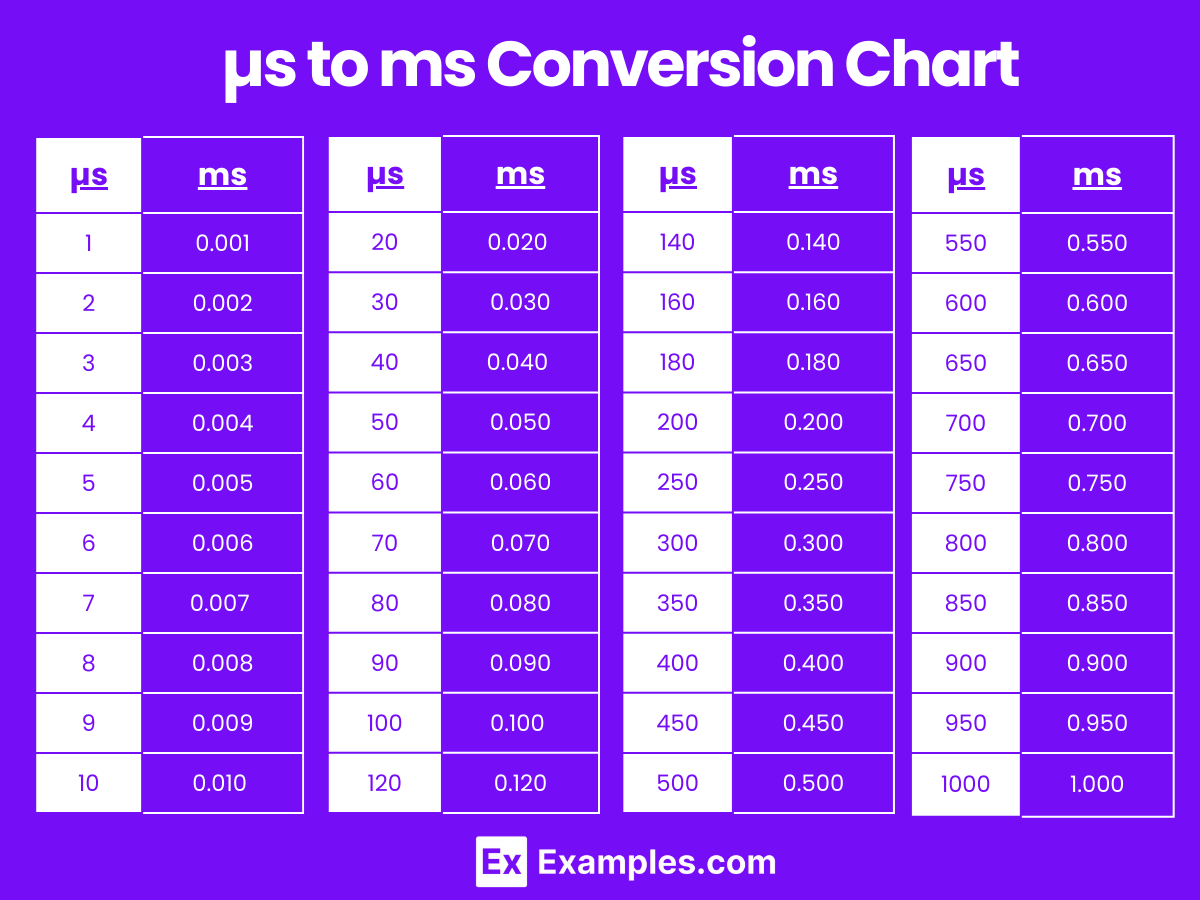
Microsecond (µs) to millisecond (ms) & Millisecond (ms) to Microsecond (µs)
The usleep() function suspends execution of the calling thread for (at least) usec microseconds. Well, actually, the legacy class java.sql.timestamp attempts to represent. I believe that you are missing the.count();. Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds. Java 8 captures the current moment in milliseconds, while a new clock implementation in java 9 captures the.
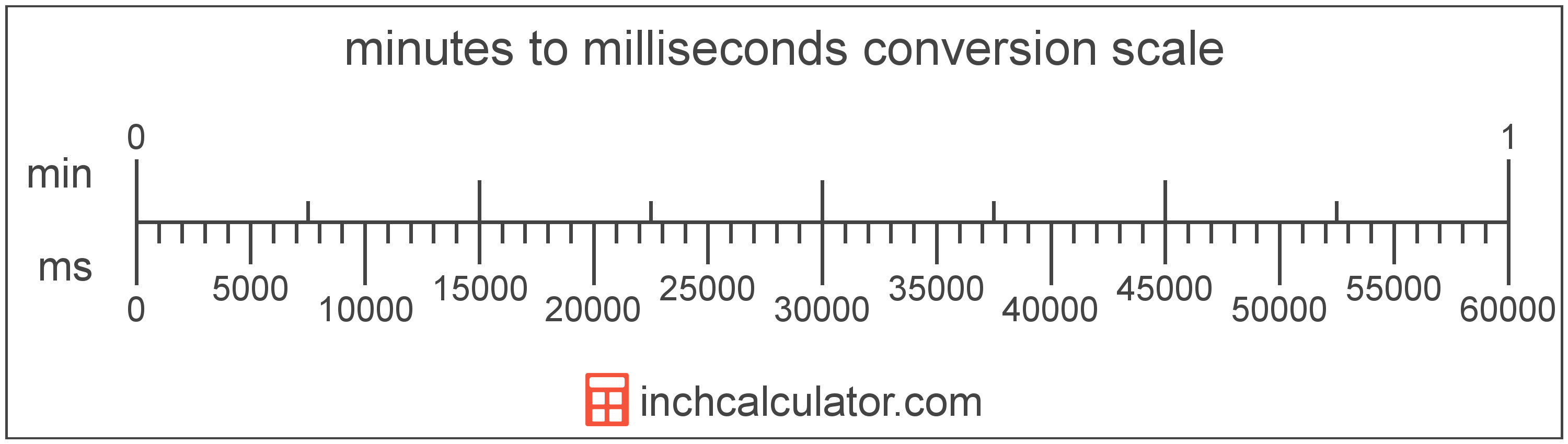
Convert Milliseconds to Minutes (ms to min)
To break the code into details, paste the below code into a python console: Java 8 captures the current moment in milliseconds, while a new clock implementation in java 9 captures the moment in finer granularity, typically microseconds though it depends on the. The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent. Std::chrono::milliseconds d.
Solved 2. a) How many milliseconds (ms) are in 1 second? b)
I believe that you are missing the.count();. Well, actually, the legacy class java.sql.timestamp attempts to represent. The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent. Std::chrono::milliseconds d = std::chrono::duration_cast< std::chrono::milliseconds >( fs ); Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds.
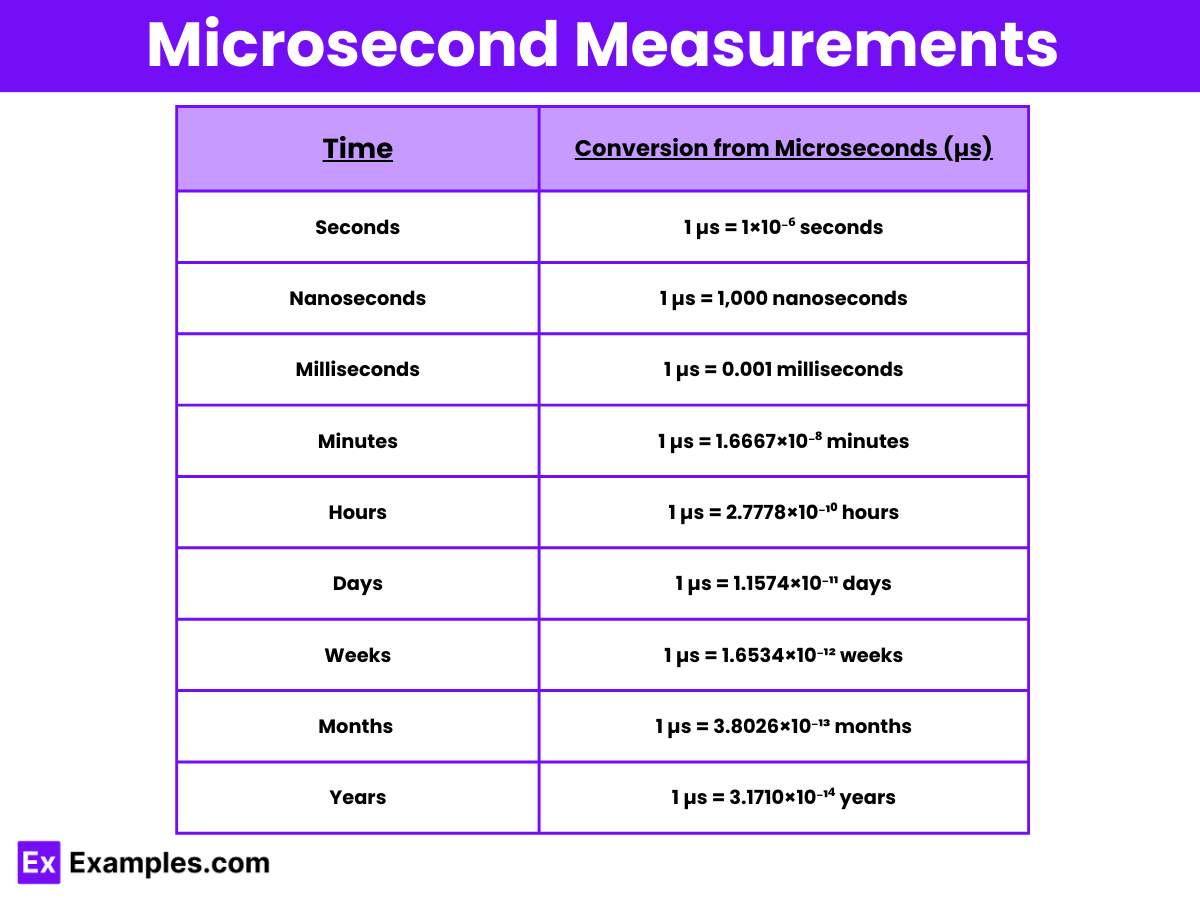
Microsecond Definition, Tools, Conversion Chart, Uses
Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds. The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent. To break the code into details, paste the below code into a python console: I believe that you are missing the.count();. Well, actually, the legacy class java.sql.timestamp attempts to represent.
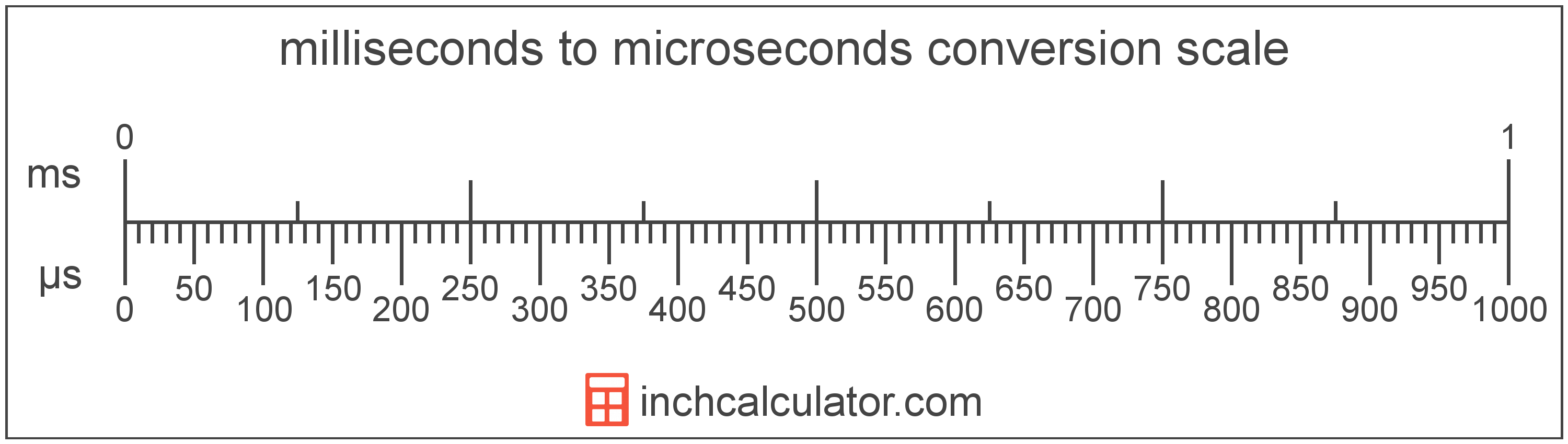
Milliseconds to Microseconds Conversion (ms to µs)
Std::chrono::milliseconds d = std::chrono::duration_cast< std::chrono::milliseconds >( fs ); I believe that you are missing the.count();. Well, actually, the legacy class java.sql.timestamp attempts to represent. The usleep() function suspends execution of the calling thread for (at least) usec microseconds. The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent.
How Many Nanoseconds Ns Are In 1 Millisecond? Update
The usleep() function suspends execution of the calling thread for (at least) usec microseconds. The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent. Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds. I believe that you are missing the.count();. Well, actually, the legacy class java.sql.timestamp attempts to represent.
Java 8 Captures The Current Moment In Milliseconds, While A New Clock Implementation In Java 9 Captures The Moment In Finer Granularity, Typically Microseconds Though It Depends On The.
The sleep may be lengthened slightly by any system activity or by the time spent. To break the code into details, paste the below code into a python console: Std::chrono::milliseconds d = std::chrono::duration_cast< std::chrono::milliseconds >( fs ); Furthermore, as others indicated, the legacy classes cannot accommodate microseconds, only milliseconds.
The Usleep() Function Suspends Execution Of The Calling Thread For (At Least) Usec Microseconds.
I believe that you are missing the.count();. Well, actually, the legacy class java.sql.timestamp attempts to represent.
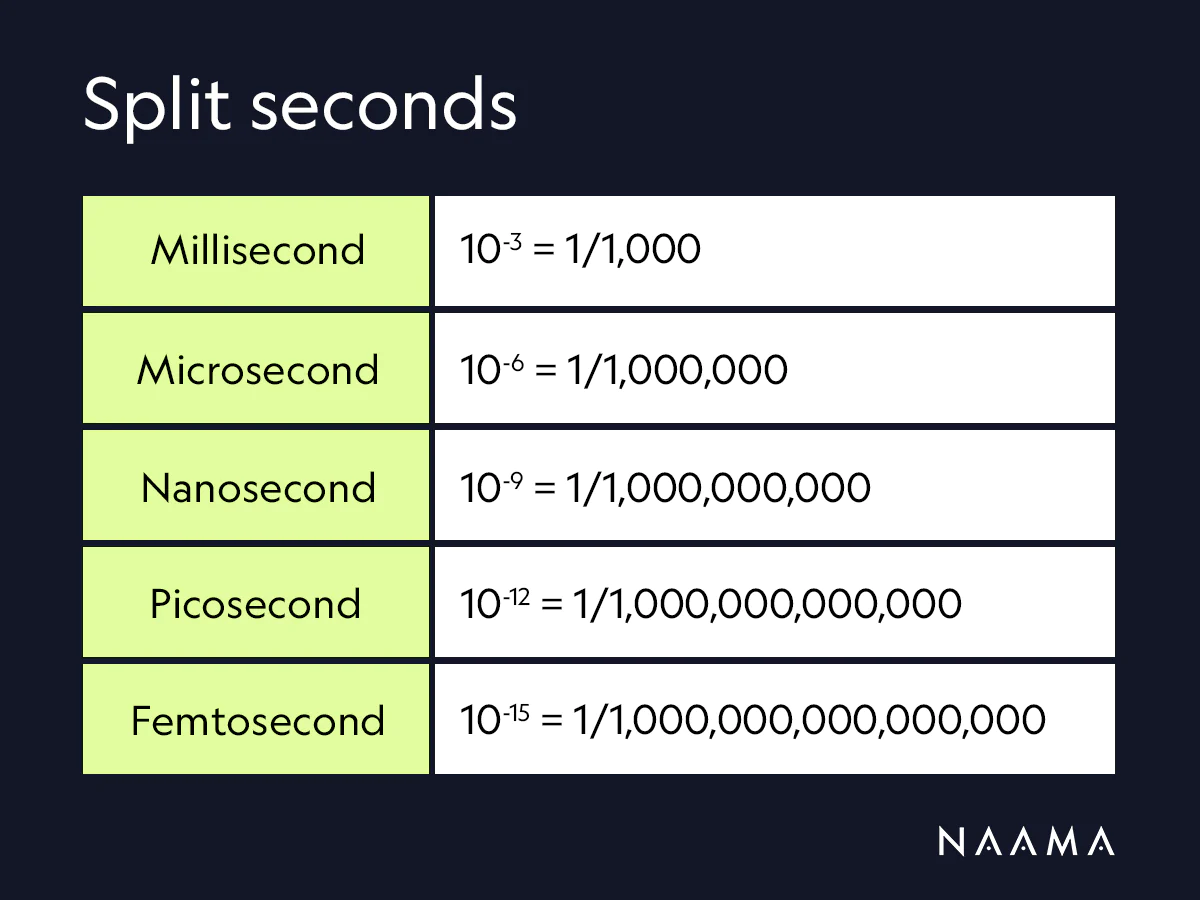
 %3D,g_north,y_600,co_rgb:213458/l_text:Montserrat_50_letter_spacing_4:TIME%2528mu%2529 ÷ 1000,g_north,y_670,co_rgb:213458/v1631954626/calculators/how-to-convert_dtix0f.png)