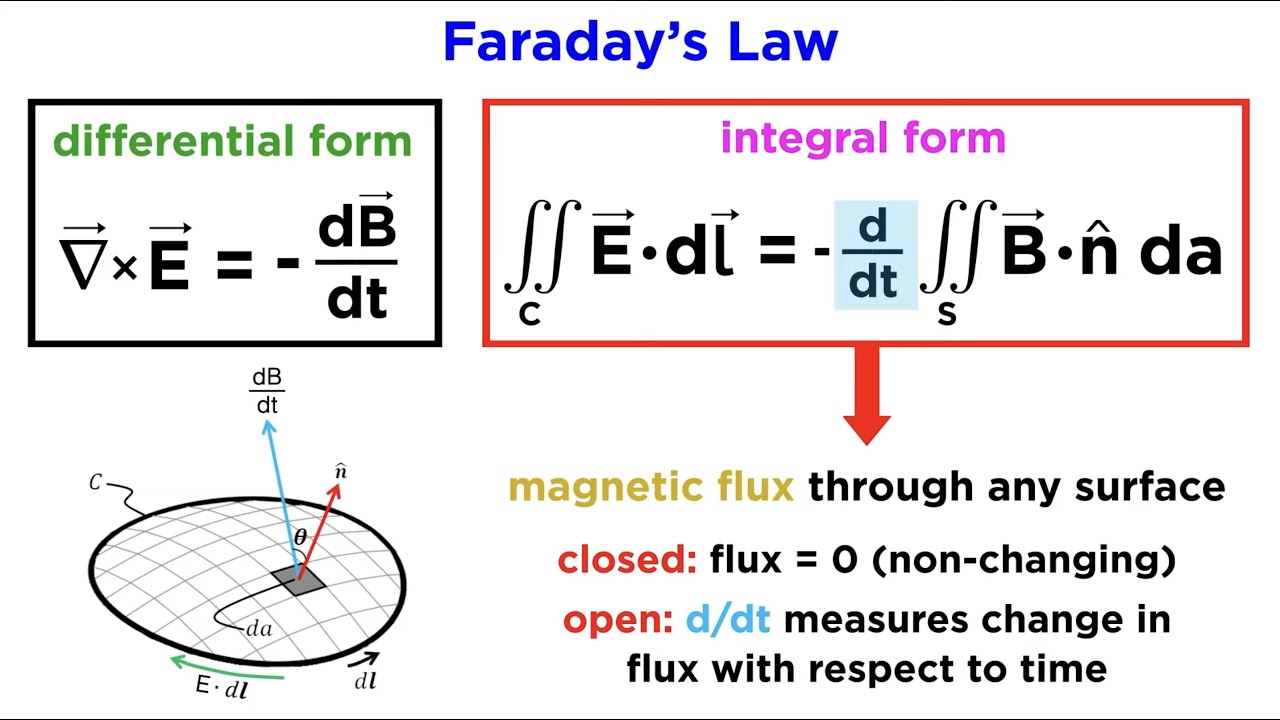
Faraday S Law Integral Form - The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=.
Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric.
Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies.
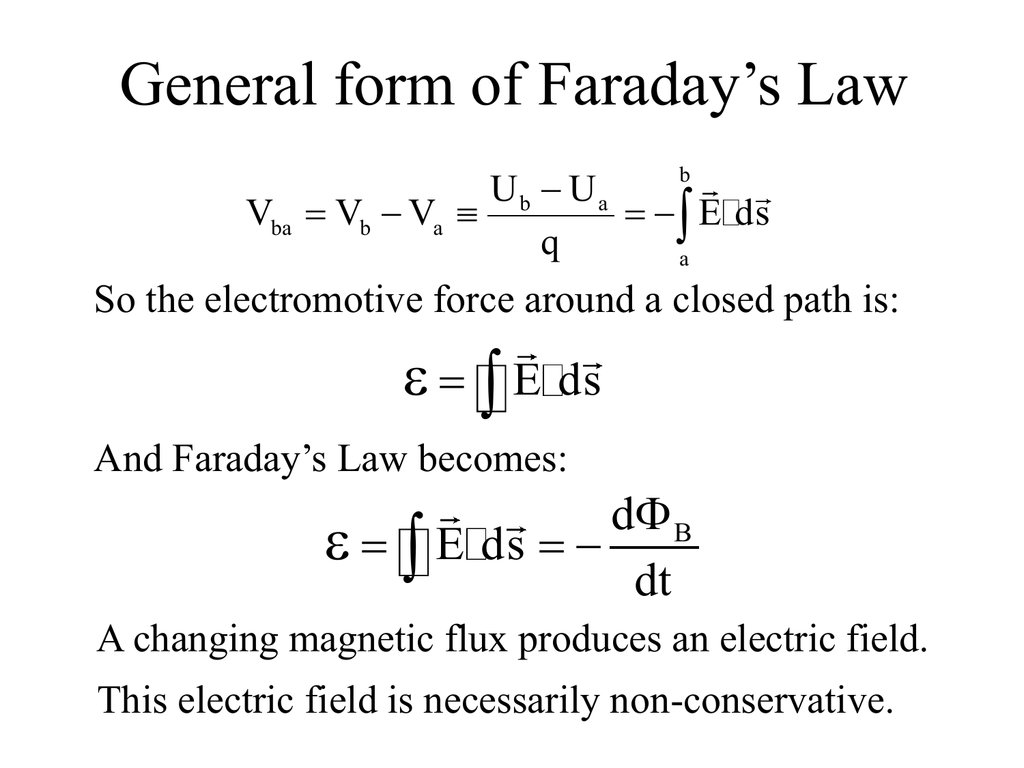
General form of Faraday’s Law
Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: Let's consider both the integral and.
Faraday's Law Understanding the Alternative (Integral Form)
Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form.
Faraday Law, standard (integral form) Physics and mathematics
Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law: The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the.
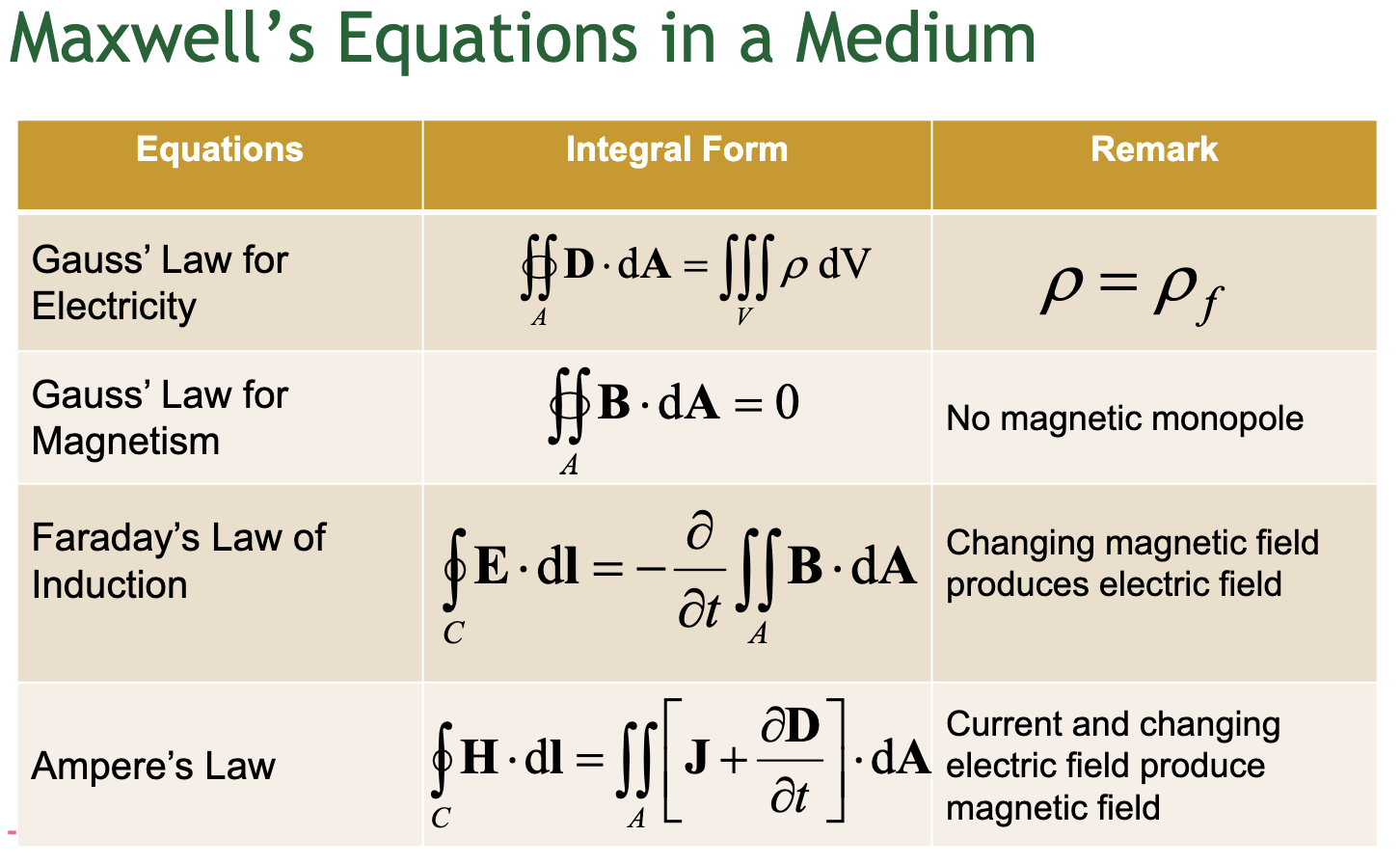
Solved Maxwell's Equations in a Medium Equations Integral
The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law.
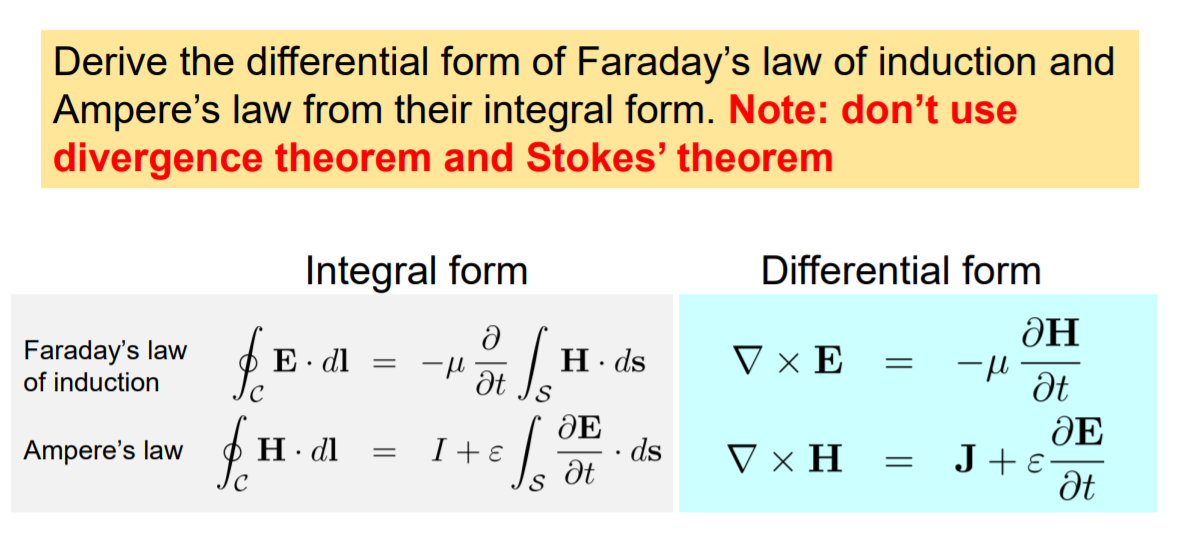
Solved Derive the differential form of Faraday's law of
Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Let's consider both the integral and differential equations.
Electrical and Electronics Engineering Faraday's Law
The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and.
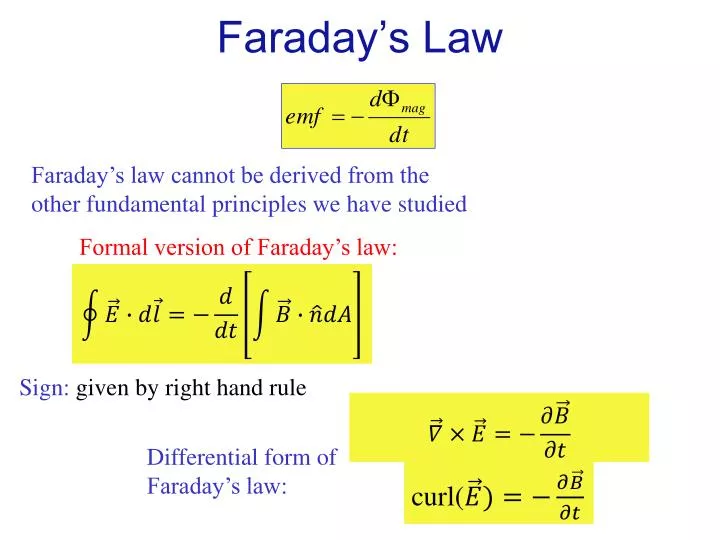
PPT Faraday’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3607741
The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric. Faraday's law of induction explains.
Maxwell’s Equations Part 3 Faraday’s Law YouTube
The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the.
Field Integral Equation Derivation Tessshebaylo
Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law of induction may be stated as follows: Using stokes’ theorem, this law can be written in integral form as \begin {equation} \label {eq:ii:17:2} \oint_\gamma\flpe\cdot d\flps=. Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will.
Faraday's Law Calculations
The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law of induction.
Using Stokes’ Theorem, This Law Can Be Written In Integral Form As \Begin {Equation} \Label {Eq:ii:17:2} \Oint_\Gamma\Flpe\Cdot D\Flps=.
Faraday's law of induction explains that a changing magnetic flux can induce a current in a loop of conducting material, and quantifies. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): The induced emf ε in a coil is proportional to the negative of the rate of change of. I want to understand how stoke's theorem shows that the integral form of faraday's law:
Faraday’s Law Of Induction May Be Stated As Follows:
Faraday’s law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric.