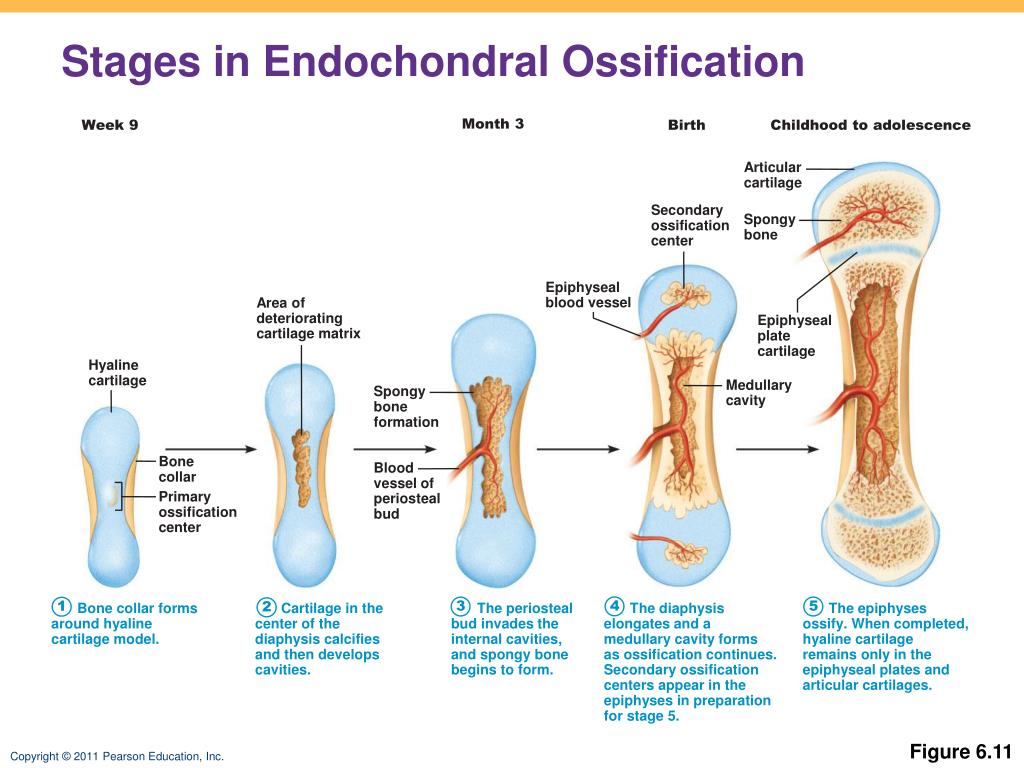
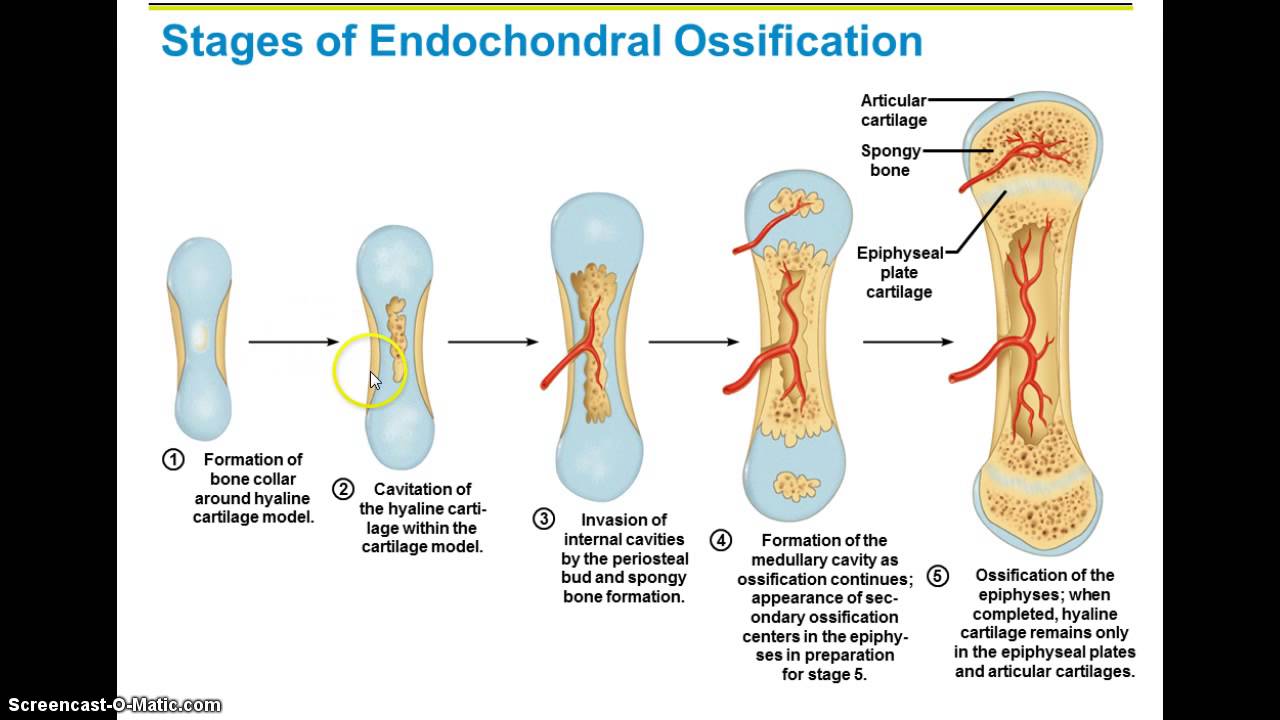
Endochondral Ossification Forms Most Bones Of The - Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone. In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. Based on the way they develop,. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4] the bones of the axial (ribs and.
In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous. Based on the way they develop,. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4] the bones of the axial (ribs and. Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone.
Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4] the bones of the axial (ribs and. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone. In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. Based on the way they develop,. Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous.
Pin on Sciencey Stuff
Based on the way they develop,. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4] the bones of the axial (ribs and. In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. Most bones in.
12 Endochondral Ossification Forms Most Bones Of The
Based on the way they develop,. Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone. In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous.
12 Endochondral ossification forms most bones of the skeleton and
Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4] the bones of the axial (ribs and. Based on the way they develop,. Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced.
Endochondral Ossification Vs Intramembranous Ossification
In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. Based on the way they develop,. Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone. Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous.
12 Endochondral Ossification Forms Most Bones Of The
Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. Based on the way they develop,. Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous. In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone.
Bone Formation by Endochondral Ossification Anatomy and Physiology JoVe
Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous. Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4] the bones of the axial (ribs and. Based on the way they develop,. In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down,.
Endochondral Ossification
Based on the way they develop,. Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone. Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created.
Endochondral Ossification (Bone Formation) Diagram Quizlet
Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous. Based on the way they develop,. Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4] the bones of the axial.
Endochondral Ossification Part 1 203 plays Quizizz
Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous. In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. Based on the way they develop,. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4] the bones of the axial (ribs and. Forms the flat bones of the.
Stages of Intramembranous Ossification n n An ossification
Forms the flat bones of the skull, face, jaw, and center of clavicle. Based on the way they develop,. Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous. In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4].
Forms The Flat Bones Of The Skull, Face, Jaw, And Center Of Clavicle.
In endochondral ossification, as masses of ______ cartilage breaks down, ______ deposit bone in the spaces created. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, [4] the bones of the axial (ribs and. Based on the way they develop,. Most bones in the body are formed by intramembranous.