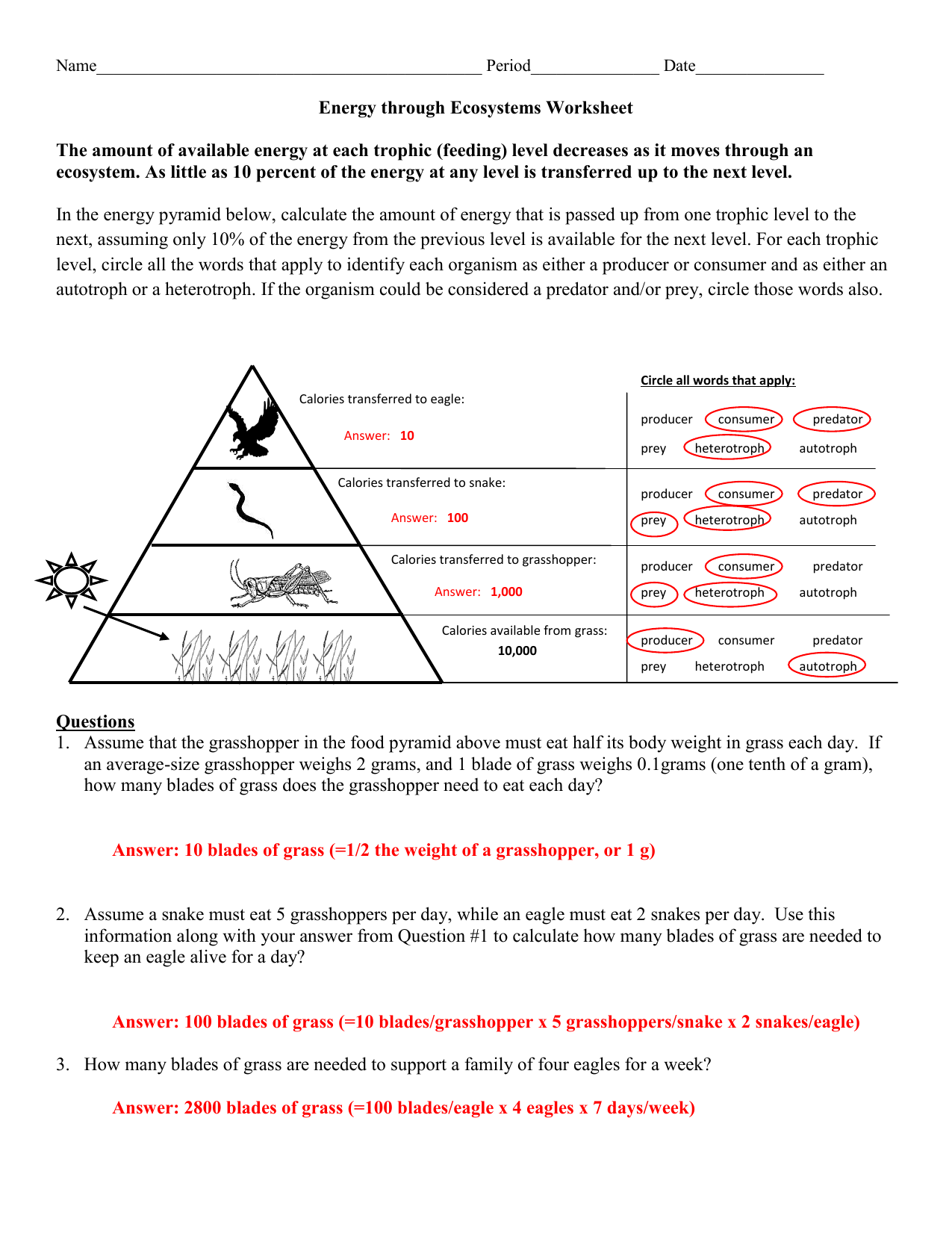
Ecology Energy Pyramid Worksheet - Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location on the energy pyramid. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,. Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on.
Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location on the energy pyramid. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,. First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”.
Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”. Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location on the energy pyramid. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,.
[Solved] . food web and energy pyramid worksheet . Saved v Search (Alt
First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. Place the organisms.
Energy Pyramid 7014424 kimdease Live Worksheets
In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,. Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the.
Ecology Food Web and Ecological Pyramids Worksheets Teaching Resources
In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,. Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location on the energy pyramid. Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”.
Energy Pyramid Worksheets Free Printables Worksheets Library
Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,. Energy pyramids show the loss.
Energy Pyramid Model Activity for Ecosystems Energy pyramid, Pyramid
Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location on the energy pyramid. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,. Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. Give one example of a food chain.
30++ Energy Pyramid Worksheet Worksheets Decoomo
First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location on the energy pyramid. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,. Energy.
Exercise2 EarthScience PDF Food Web Systems Ecology Worksheets
Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,. Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location.
Building An Energy Pyramid Worksheet Answer Key Kidsworksheetfun
In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy,. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”. Place the organisms in each food.
😊 Ecological energy pyramid worksheet. Energy Pyramids Worksheets. 2019
Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. Energy pyramids show the loss of energy through an ecosystem. Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location on the energy pyramid. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. First pyramid side (next.
30 Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answers Pogil support worksheet
Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location on the energy pyramid. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000.
In An Ecological Pyramid, What Happens To Energy,.
Place the organisms in each food chain into the proper location on the energy pyramid. Energy pyramid •label trophic levels (producers, primary (1°) consumer, secondary (2°) consumer, tertiary (3°) consumer) •start with 100,000 j on. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. First pyramid side (next to tab), at the bottom of the first layer label “autotrophs, heterotroph”.